Rekindle your Light, Start your recovery journey today!
Nationwide Addiction Treatment Center Network
Welcome to Lumina Recovery
Residential Inpatient and Outpatient Treatment Nationwide
Lumina Recovery, headquartered in Los Angeles, offers compassionate inpatient and outpatient addiction treatment, including medication-assisted treatment (MAT). We have treatment centers available to support your healing, all across the United States.
We are committed to transforming lives and inspiring change through personalized recovery by addressing the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of addiction to drugs and alcohol.
Your journey is unique to you. The care you receive should be, too.
Addiction Treatment Programs
Lumina Recovery addiction treatment centers are built with an intimate, personalized approach and exceptional aftercare support, providing ongoing assistance and guidance beyond the rehabilitation process.

Detox

Detox
Lumina Recovery offers residential medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for alcohol and drug detox in a safe, serene environment. Alcohol detox and drug detox are the crucial first steps of addiction treatment. At each of our locations across the nation, we provide a safe environment for drug and alcohol detox, guiding individuals through the challenging process of recovery, setting the foundation for their transformative journey to sobriety.
Our expert-led detoxification programs prioritize individualized care, integrating evidence-based therapies and holistic interventions to ensure a comprehensive approach that meets the unique needs of each client.

Inpatient

Inpatient
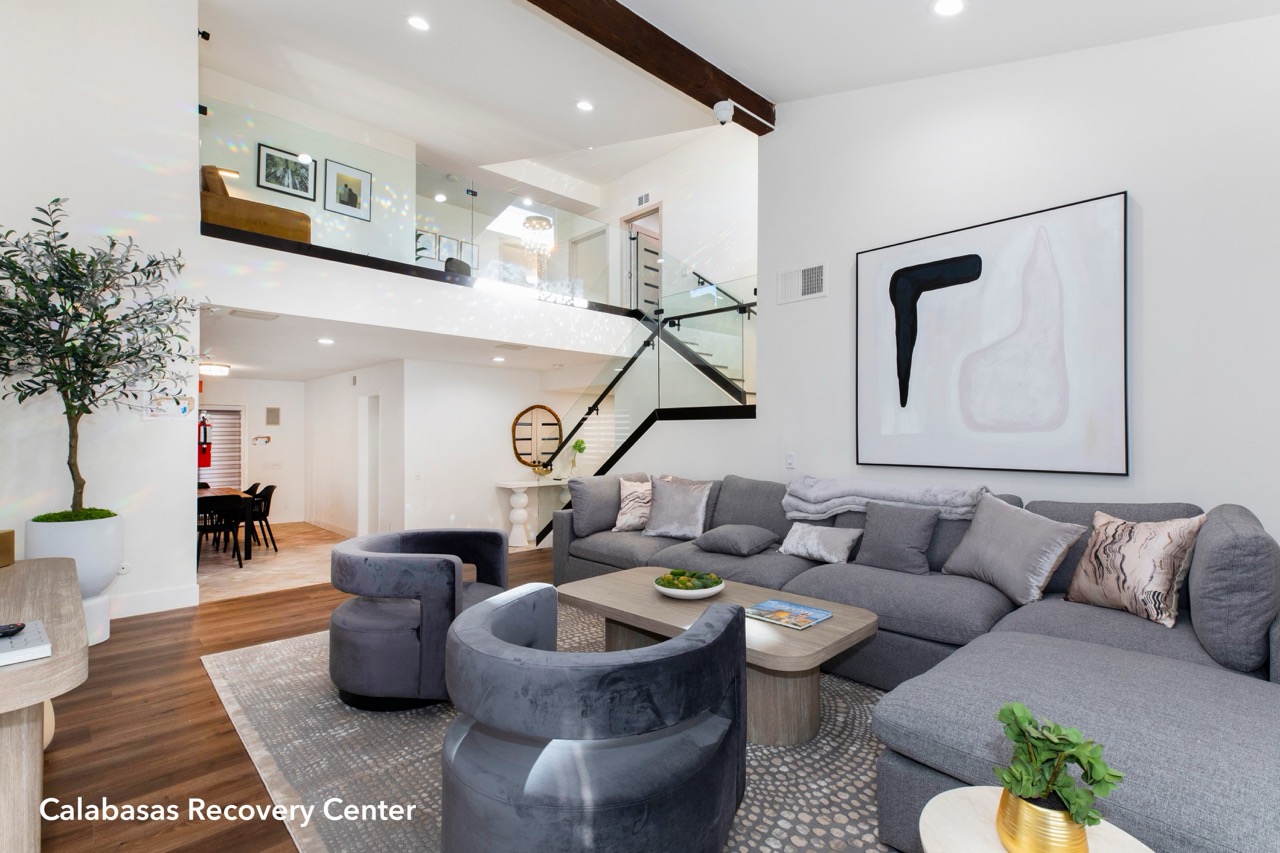
Our serene, state-of-the-art alcohol and drug rehabs in Los Angeles and nationwide provide a supportive setting with private accommodations for those seeking comprehensive addiction treatment. With compassionate care and therapeutic support, we guide patients from alcohol detox and drug detox toward lasting recovery.
We provide round-the-clock care ensuring patients’ physical and emotional well-being during their 30-day residential stay (or longer if needed). Our detox and inpatient drug rehabs in Los Angeles and across the country minimize exposure to external triggers, fostering a secure space for healing and self-discovery.

Outpatient
Outpatient
Our nationwide and Los Angeles drug rehab and alcohol rehab outpatient programs offer flexible solutions for recovery, empowering individuals to maintain their daily lives while receiving expert therapeutic support including therapy, one-on-one support, and telehealth options.
Compassion and inspiration drive our commitment to healing. We take into consideration the challenges you or a loved one may face as you embark on your recovery from drugs or alcohol and do our best to help you navigate those hurdles, put yourself first, and balance work, family, etc. We offer partial hospitalization programs (PHP) and intensive outpatient programs (IOP) for those in need of a bit more structure and a higher level of care.
Our Addiction Treatment and Mental Health Programs
Whether you’re seeking care for yourself or a loved one, Lumina Recovery’s national drug and alcohol rehabs are some of the best and most coveted drug and alcohol treatment programs in the country.
Regain control of and enjoy your life.
National Inpatient Drug Rehab and Outpatient Drug Rehab Options
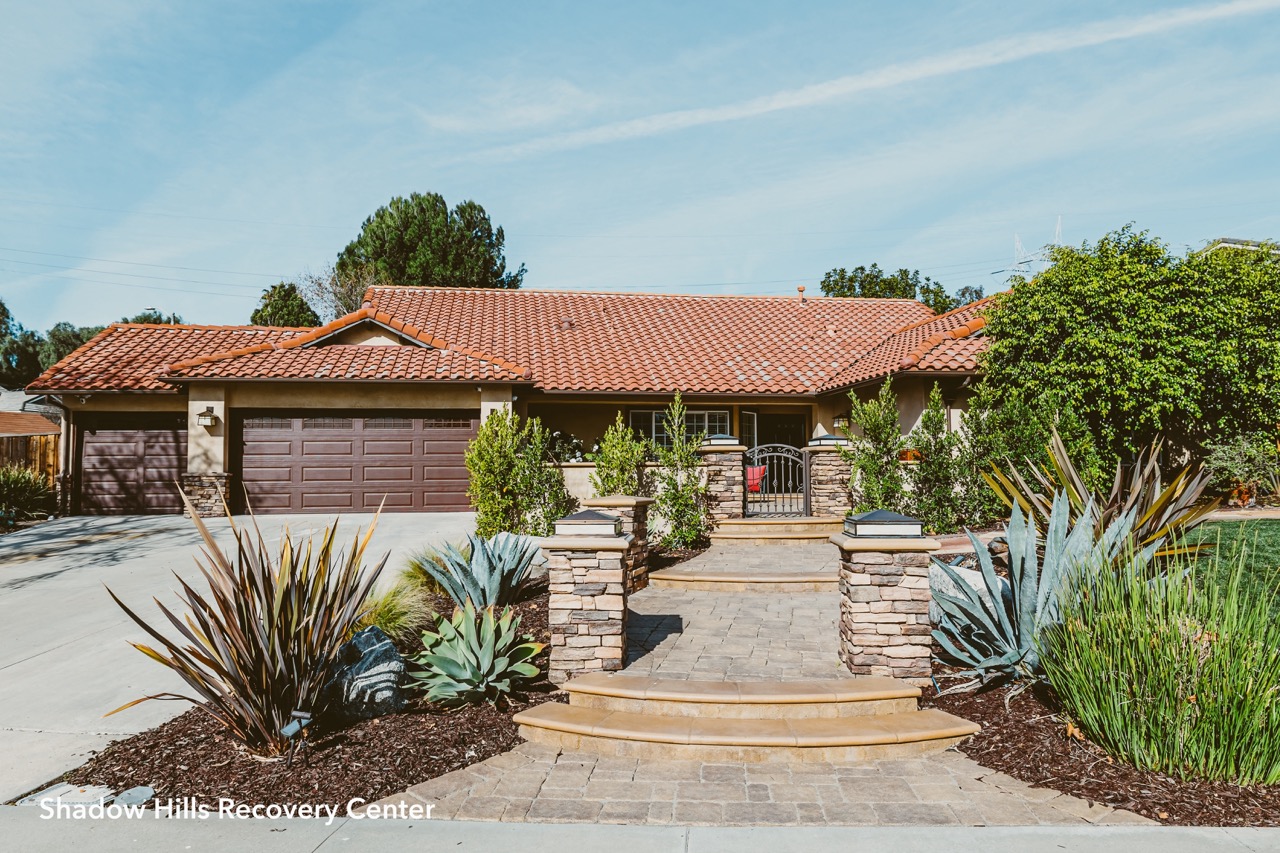
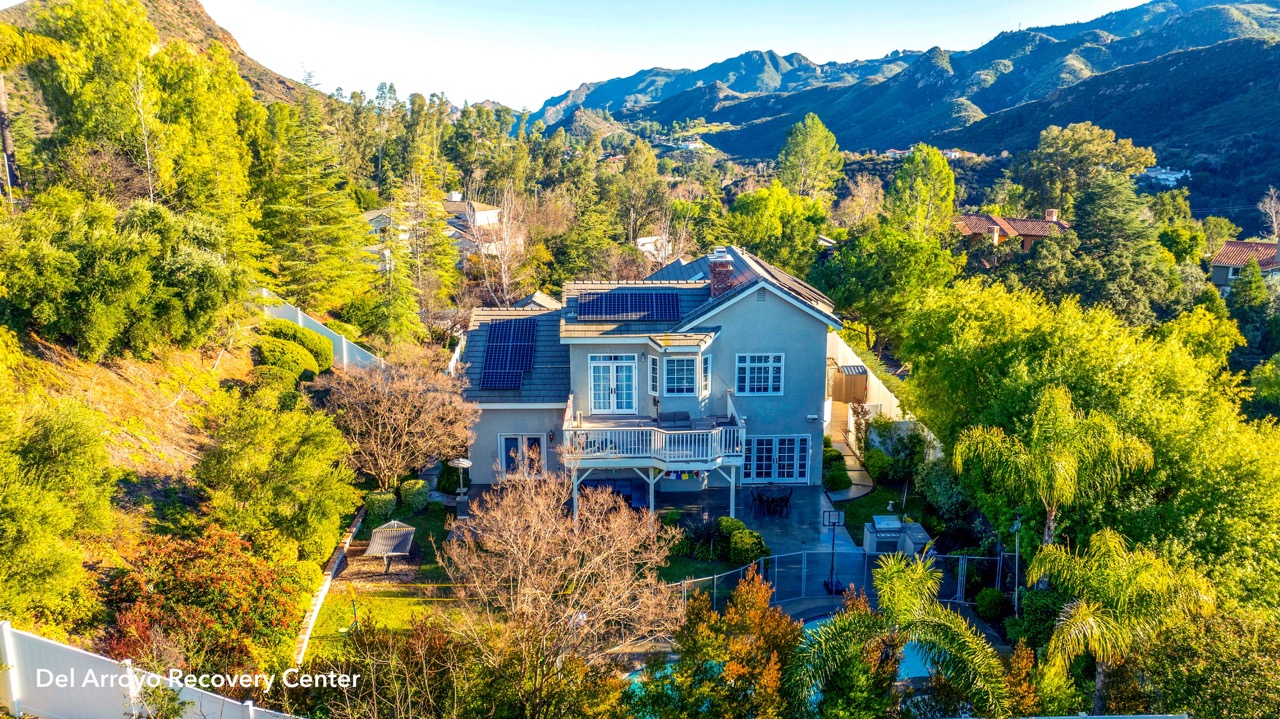
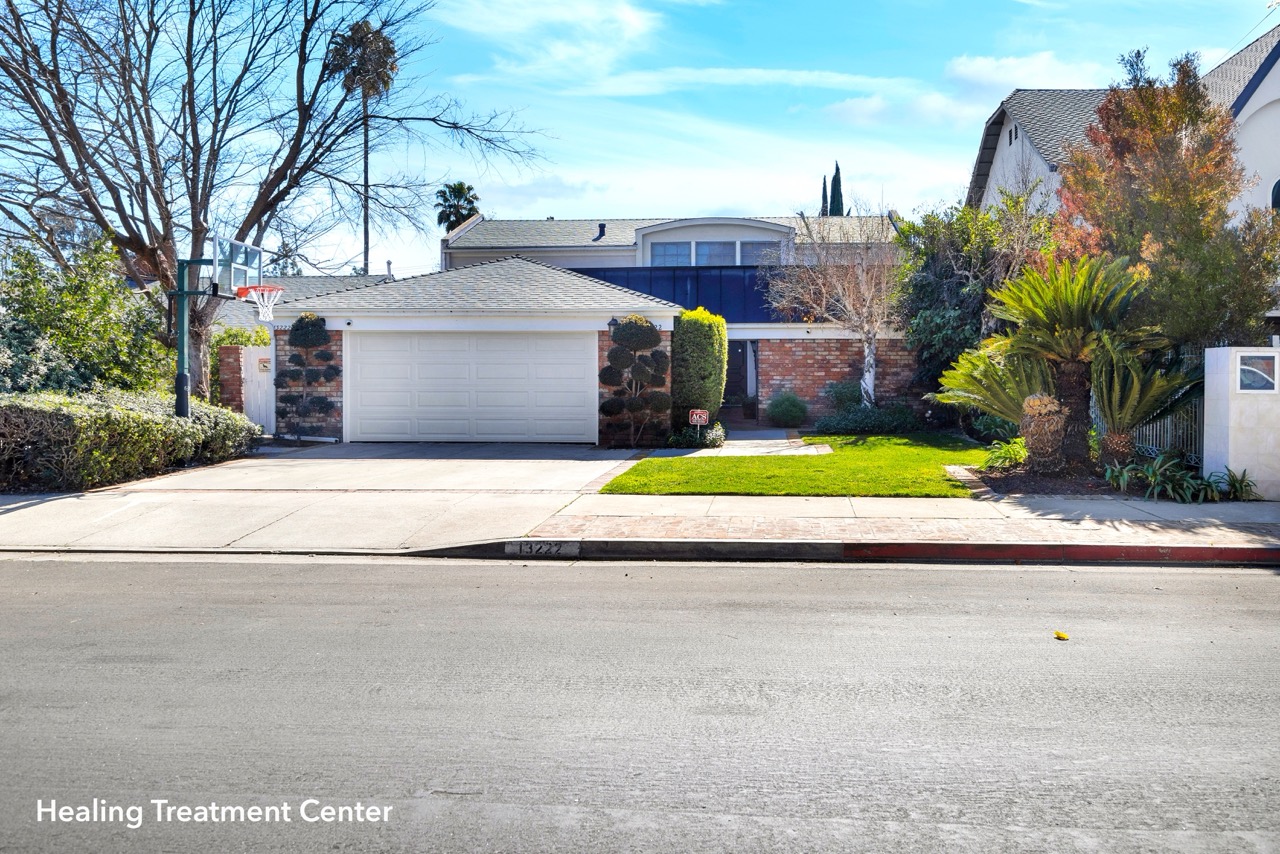
We carefully help you choose the correct rehab that will best benefit you with its healing surroundings and restorative qualities, ensuring that you or a loved one can find solace and support in a tranquil atmosphere.
Inpatient Facilities
Outpatient Facilities
You deserve affordable care.
Insurance We Accept at Our Addiction Recovery Centers
At Lumina Recovery, we promote inclusivity and support lasting recovery. We believe that access to addiction treatment should be attainable for all. We accept most major health insurance providers, ensuring that quality addiction treatment is within reach for as many individuals as possible.
There is no act braver than asking for help.
What Types of Addictions Do We Treat?
Our comprehensive addiction treatment programs are designed to address the unique challenges associated with each addiction, ensuring everyone receives the specialized care they need for successful recovery. Lumina Recovery’s alcohol and drug rehabs nationwide is dedicated to offering detoxification and treatment for a wide range of addictions, including those involving:
What Types of Addictions Do We Treat?
Our comprehensive addiction treatment programs are designed to address the unique challenges associated with each addiction, ensuring everyone receives the specialized care they need for successful recovery. Lumina Recovery is dedicated to offering detoxification and treatment for a wide range of addictions, including those involving:
Alcohol
Abuse
Benzodiazepine
Abuse
Cocaine
Abuse
Opioid
Abuse
Methamphetamine
Abuse
Prescription Drug
Abuse
Our patients say it best
Testimonials

No matter what—YOU matter.
Take your next step towards recovery
Call us Today!
If we haven’t answered your question below, please reach out to us.
Frequently Asked Questions
We understand that you and your family may be going through a challenging period. The process of comprehending the treatment options for alcoholism, drug addiction, and mental health conditions that we address can be quite complex, and it may raise numerous questions.
An inpatient rehab treatment program involves residing at a facility while receiving intensive, 24/7 care, making it suitable for severe cases of drug and alcohol addiction. Outpatient treatment allows individuals to live at home or be in sober living and attend therapy sessions part-time, offering more flexibility for those with less severe substance abuse and/or strong support systems.
Alcohol and drug detox, inpatient drug rehab, inpatient alcohol rehab, outpatient drug rehab, and outpatient alcohol rehab treatment for prescription drugs, meth, heroin, fentanyl, and other substances typically incorporate a range of evidence-based therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), group therapy, family therapy, and individual counseling. The specific therapies may vary by facility, but they all aim to address the underlying causes of addiction.
The duration of inpatient alcohol treatment or drug treatment can vary from a few weeks to several months, depending on individual needs. Outpatient programs vary in intensity, with some lasting for several months, while others extend to a year or more, allowing for a gradual transition to independent recovery. Our caring experts will help determine the best addiction treatment center for you or a loved one.
Both inpatient and outpatient rehab centers for drug and alcohol treatment should offer aftercare planning and relapse prevention strategies. This may include ongoing therapy, alumni programs, and access to support groups, helping individuals maintain sobriety after completing the initial treatment phase.
At Lumina Recovery’s rehab centers, we take immense pride in our commitment to personalized treatment, maintaining a remarkably low staff-to-patient ratio. This ensures that each individual receives the focused attention, support, and guidance needed for their unique path towards lasting recovery from drugs and alcohol.















