
Our Addiction Resources
Navigating the world of addiction and recovery can be overwhelming. We’re here to provide clear, compassionate education and guidance. From practical advice for maintaining sobriety to informational guidance on the long-term effects of substance abuse, our content is a beacon of hope and understanding.
Our Team is Ready are ready to take your call
Call us Today!
or we can call you. Fill out form below
Our Blog

What Is an Alternative Sentencing Program?
An alternative sentencing program is a judicial approach that provides offenders with rehabilitation-focused options instead of incarceration. These programs aim to address the root causes of criminal behavior, such as substance use disorders and mental health challenges, while reducing recidivism and easing the burden on the criminal justice system.
For those struggling with addiction, or their loved ones seeking guidance, understanding how alternative sentencing works can provide hope and direction.
What Is Alternative Sentencing?
Alternative sentencing programs are structured interventions designed to divert individuals found guilty of non-violent crimes from traditional incarceration into supervised treatment, rehabilitation, or community-based programs.
For those with drug-related offenses, these programs aim to address the underlying causes of addiction, reduce repeat offenses, and support long-term recovery. Rather than punishment, they emphasize rehabilitation, equipping individuals with tools for a healthier future.
These initiatives hold individuals accountable while providing them with opportunities for personal growth, ultimately reducing their likelihood of reoffending.
4 Types of Alternative Sentencing Programs
Alternative sentencing programs offer various pathways for individuals with substance use disorders or co-occurring mental health conditions. Some of the programs available for those with drug-related offenses include:
1. Drug Courts
Drug courts are specialized judicial programs that offer individuals struggling with substance use disorders a structured recovery path. Instead of serving jail time, offenders undergo supervised treatment, counseling, and frequent drug testing.
2. Veterans Courts
Veterans courts cater specifically to military veterans who have committed offenses, often as a result of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), substance abuse, or other service-related challenges. These programs connect veterans with counseling, treatment services, and peer support networks.
3. Co-Occurring Disorders Courts
For individuals with both addiction and mental health disorders, co-occurring disorders courts focus on treatment by ensuring appropriate psychiatric care, counseling, and medication management. These courts work to address the underlying mental health issues contributing to criminal behavior, thereby reducing future offenses.
4. Second Chance Women’s Re-Entry Courts
These programs are designed specifically for women who have been involved in the criminal justice system due to neglectful parenting, criminal behavior, and drug abuse. They provide trauma-informed care, substance abuse and mental health treatment, job training, education programs, and parenting and life skills development.
Eligibility Criteria for Alternative Sentencing
Eligibility for an alternative to incarceration programs varies by state and depends on several factors, including:
- Nature of the offense such as possession, DUI, or minor drug-related crimes
- First-time or low-level repeat offenders
- Willingness to participate in rehabilitation programs
- Diagnosis of substance use disorder or dual diagnosis
Process of Alternative Sentencing
The alternative sentencing process involves several key steps to ensure that eligible offenders receive appropriate rehabilitation and supervision while fulfilling their legal obligations.
- Assessment: Before being placed in an alternative sentencing program, an offender undergoes an assessment to determine their eligibility. This may involve reviewing criminal history, conducting psychological evaluations, and assessing substance use disorders.
- Program Assignment: Based on assessment results, the offender is assigned to a suitable program, such as a drug court, veterans court, or community service.
- Monitoring and Compliance: Participants are required to comply with strict guidelines, including court appearances, counseling sessions, random drug tests, or community service requirements. Non-compliance may result in harsher penalties or a return to traditional sentencing.
- Completion and Outcomes: Successful completion of the program can result in benefits such as reduced charges, expunged records, or the opportunity to reintegrate into society with improved personal stability and job prospects.

5 Benefits of Alternative Sentencing
The benefits of sentencing alternative programs extend beyond the individual offender, positively impacting the criminal justice system and society as a whole.
1. Supports Long-Term Sobriety
These programs address the root causes of addiction rather than merely punishing the behavior, helping individuals develop coping skills for long-term recovery.
2. Reduces Recidivism Rates
Individuals who complete drug court and similar programs are less likely to reoffend compared to those who serve traditional sentences.
According to a report from the Countywide Criminal Justice Coordination Committee (CCJCC), more than 70% of individuals who successfully completed a drug court program remained conviction-free for at least five years after graduation.1
3. Provides Access to Comprehensive Treatment
Alternative sentencing often includes individual therapy and mental health services, ensuring holistic care for addiction and co-occurring disorders.
4. Keeps Families Together
Avoiding incarceration allows individuals to stay connected with their families, maintain employment, and contribute positively to their communities.
5. Eases the Burden on the Criminal Justice System
By diverting non-violent drug offenders from prisons into treatment, these programs help reduce overcrowding and save taxpayer money.

FAQs
What is alternative sentencing?
Alternative sentencing refers to judicial programs that provide rehabilitation-focused sentencing alternatives rather than traditional incarceration. These programs address the root causes of criminal behavior, particularly addiction and mental health disorders.
What crimes qualify for alternative sentencing?
Typically, non-violent offenses, including drug-related crimes, minor theft, and certain DUIs, may qualify. Eligibility is determined on a case-by-case basis.
How do drug courts help offenders with addiction?
Drug courts provide structured recovery programs, including treatment, therapy, and strict accountability measures, to support sobriety and prevent future offenses.
Can alternative sentencing lead to a criminal record being expunged?
In some cases, successful completion of an alternative sentencing program may result in reduced charges or expungement, depending on state laws.
What happens if someone violates the terms of an alternative sentencing program?
Non-compliance may lead to harsher penalties or a return to traditional sentencing.
Start Rehabilitation Today With Lumina Recovery
Alternative sentencing programs offer individuals struggling with addiction a chance to receive necessary treatment while avoiding incarceration. By focusing on rehabilitation, these programs support long-term recovery and a better future.
Lumina Recovery’s dual diagnosis programs provide integrated care for substance use and mental health disorders, ensuring a well-rounded recovery approach. We also offer outpatient treatment for individuals involved in alternative sentencing, providing therapy, counseling, and relapse prevention support.
If you or a loved one is facing legal challenges due to addiction, contact Lumina Recovery today to explore treatment options and take the first step toward healing.
Source:
- Los Angeles County District Attorney’s Office. Alternative Sentencing Courts.

7 Facts to Celebrate National Drug and Alcohol Facts Week
National Drug and Alcohol Facts Week (NDAFW) is an annual observance dedicated to spreading awareness about the science and realities of drug and alcohol use. While it was originally created to educate youth, the information shared during this week is important for individuals of all ages.
Whether you’re a college student, a working professional, or someone in long-term recovery, understanding facts about addiction can help you or a loved one make informed choices.
This year, National Drug and Alcohol Facts Week takes place from March 17-23, 2025, making it the perfect time to educate yourself on the risks of drug and alcohol use and the importance of seeking help when needed.
History and Purpose of National Drug and Alcohol Facts Week
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) launched National Drug and Alcohol Facts Week in 2010 to educate teens about the science behind drug use and addiction. In 2016, the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) joined the effort, expanding its focus to include alcohol education.1
While much of the information shared during NDAFW is geared toward young people, the facts about addiction are relevant for all age groups. Substance use disorders impact people of all backgrounds and understanding addiction facts can lead to smarter choices, early intervention, and successful recovery.

7 Important Facts About Addiction and Substance Use
Whether you’re managing work stress, social pressures, or personal struggles, knowing these key addiction facts can help you make informed decisions.
1. Alcohol Is the Most Commonly Misused Substance
While underage drinking is often discussed, alcohol misuse remains a leading cause of preventable deaths in the U.S. The CDC reports that excessive alcohol use contributes to 178,000 deaths annually, linked to liver disease, heart problems, and accidents.2
2. Addiction Can Develop at Any Age
A common addiction myth is that substance use disorders only affect younger people. In reality, addiction can start at any stage of life. Stress, trauma, mental health struggles, and social drinking that escalate over time can all contribute to dependency.
3. Mixing Alcohol With Prescription Medications Can Be Deadly
Many people take prescription medications, but few realize that combining them with alcohol can be dangerous. Medications like opioids, benzodiazepines (Xanax, Valium), and antidepressants can cause life-threatening side effects when mixed with alcohol, including respiratory failure, blackouts, and overdose.
4. Opioid Addiction Affects People of All Backgrounds
Many people become dependent on prescription painkillers after surgery, injury, or chronic pain treatment. In 2022, approximately 81,800 overdose deaths involved opioids.3
Even those who don’t consider themselves “regular users” are at risk if they take opioids without medical supervision or combine them with other substances. Being aware of addiction facts can help reduce the likelihood of accidental overdose.
5. Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders Are Closely Linked
Substance use often starts as a way to cope with stress, anxiety, depression, or past trauma, but it can quickly turn into a harmful cycle.
The 2023 National Survey on Drug Use and Health reported that 35% of individuals with mental health disorders also have a substance use disorder, and vice versa.4 This is why dual diagnosis treatment, which addresses both addiction and co-occurring mental health issues, is critical for long-term recovery.
6. High-Stress Lifestyles Can Increase the Risk of Substance Use
Many people facing overwhelming work, financial, and personal pressures turn to substances as a way to cope. High-stress environments, such as demanding careers, long work hours, or academic challenges, increase the risk of substance misuse. Common risk factors include:
- Using alcohol to “unwind” after work
- Misusing prescription stimulants (such as ADHD medications) to stay productive
- Using opioids for chronic pain without medical supervision
While stress is a natural part of life, self-medicating with drugs or alcohol can lead to long-term problems.
7. Recovery Is Possible at Any Stage of Life
One of the most important addiction facts to remember is that it’s never too late to seek help for addiction. Whether someone has struggled for years or is just beginning to see the warning signs of addiction, recovery is always possible.

How to Start Your Recovery Journey
Taking the first step toward recovery may seem difficult, but support is available. Here’s how to begin:
- Recognize the signs. If substance use is affecting your health, relationships, or work, it may be time for help.
- Seek professional treatment. Options like detox, inpatient rehab, and outpatient programs provide structure and support.
- Consider dual diagnosis care. If you have co-occurring mental health challenges, integrated treatment is key.
- Reach out for support. Talk to a licensed treatment center, support group, or healthcare provider for guidance.
FAQs
How can I recognize if I have a substance use problem?
If your substance use is affecting your work, relationships, or overall well-being, it may be time to seek help. Signs of addiction include increased tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, and an inability to cut back despite negative consequences.
What treatment options are available for those struggling with addiction?
Detox, residential inpatient treatment, outpatient programs, and specialized programs are available for those struggling with addiction. Dual diagnosis treatment for those facing both addiction and mental health challenges is important as well.
Is it possible to manage addiction while in college or working full-time?
Yes. Specialized college programs and outpatient treatment options allow individuals to continue their education or careers while receiving support. Flexible scheduling and telehealth services make it easier to balance recovery with daily responsibilities.
What should I do if a friend or colleague is struggling with substance use?
Express concern without judgment and encourage them to seek professional help. Providing resources and offering support can make a significant difference in their decision to seek treatment.
Take the Next Step Toward Recovery With Lumina Recovery
National Drug and Alcohol Facts Week is an opportunity to learn the truth about addiction and take proactive steps toward health and wellness. Whether you or a loved one is struggling with substance use, help is available.
At Lumina Recovery, we offer inpatient rehab and outpatient programs to help individuals overcome addiction and reclaim their lives.
Take control of your future and contact Lumina Recovery today to start your journey toward healing.
Sources:

What Is Alcohol Poisoning? Causes, Signs, and Prevention
Alcohol poisoning is a severe, potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when you consume a large amount of alcohol in a short span of time. It disrupts the central nervous system and impairs vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and body temperature regulation.
Recognizing the early signs can make all the difference, as prompt action may save a life. Whether you drink alcohol or care for someone who does, understanding how alcohol poisoning happens and knowing how to respond is essential.

The Science Behind Alcohol Poisoning
When you drink alcohol, it affects your central nervous system and slows down brain functions. The blood alcohol concentration (BAC) measures the percentage of alcohol in your blood. As the BAC rises, it increases the risk of alcohol poisoning and impairs vital functions.
Even after initial consumption, the stomach and intestines continue to absorb alcohol, further elevating the BAC and potentially overwhelming the liver. This disruption can compromise life support functions, making it critical to monitor signs like changes in body temperature and heart rate.
Causes and Risk Factors
One of the primary causes of alcohol poisoning is binge drinking. When you engage in binge drinking, you consume a large amount of alcohol in a short period. Drinking on an empty stomach can worsen the situation because it allows alcohol to be absorbed more rapidly, which increases the risk of alcohol poisoning.
This is a common issue among teens and college-age individuals who drink alcohol irresponsibly and may not yet understand the impact of their choices.
Not everyone is affected by alcohol in the same way. Factors such as body weight, metabolism, and tolerance play a role in how your body processes alcohol. Mixing alcohol with other substances can also overwhelm your system, making it essential to understand your limits and avoid behaviors that can lead to dangerous outcomes.
Signs and Symptoms of Alcohol Poisoning
Recognizing the signs of alcohol poisoning early can be life-saving. Look out for these symptoms:
Early Indicators
- Confusion: The person may seem disoriented or unable to think clearly.
- Vomiting: Repeated vomiting can signal that the body is trying to expel too much alcohol.
- Impaired Coordination: Difficulty walking or maintaining balance is a common sign.
Severe Manifestations
- Seizures: Uncontrolled convulsions may occur.
- Slow or Irregular Breathing: Breathing can become shallow or erratic, which directly affects the heart rate.
- Loss of Consciousness: An unconscious person is one of the most alarming symptoms of alcohol poisoning.
- Reduced Gag Reflex: A compromised gag reflex increases the risk of choking, so it is crucial to monitor if the person is at risk of aspirating vomit.
- Abnormal Body Temperature: A drop in body temperature can be dangerous and indicates that the body is failing to regulate itself.
Immediate Response and First Aid
If you suspect someone has alcohol poisoning, swift action is essential. Follow these steps:
Emergency Actions
- Call 911. If you see any severe symptoms such as an irregular heart rate, loss of consciousness, or a compromised gag reflex, call 911 Quick action can prevent further complications.
- Stay with the person. Remain with the individual at all times to monitor their condition. If the person becomes unconscious, it is vital that someone stays to check on them.
- Position to prevent choking. To prevent choking, gently roll the person onto their side. This position helps keep the airway clear in case their gag reflex is weak.
- Keep them warm. Ensure that the person’s body temperature is maintained while waiting for emergency services.
What to Avoid
- Do not induce vomiting. Trying to force the person to vomit can worsen the situation. The process of vomiting might lead to choking, especially if their gag reflex is not working correctly.
- Avoid cold showers or excessive cooling. Although it might seem like a way to counteract high body temperature, using cold showers or other methods of rapid cooling can be harmful.
Quick, calm, and proper first aid is vital when dealing with alcohol poisoning.

Avoiding Alcohol Poisoning and Overcoming Addiction
If you or a loved one is struggling with alcohol addiction, seeking help is a vital step toward a healthier future. Immediate medical attention is crucial when severe symptoms occur, allowing you to stabilize your condition and avoid alcohol poisoning. Once the acute phase is managed, long-term recovery focuses on addressing the underlying addiction.
A range of evidence-based treatments exists, including medically supervised detox programs, residential or outpatient care, and therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and medication-assisted treatment (MAT). These approaches help manage triggers, develop healthy coping strategies, and reduce the risk of relapse.
Recovery is a personal journey influenced by early intervention, a supportive network, and professional guidance. Taking that first step to seek help can transform your life and set you on the path to lasting wellness.
FAQs
What are the first signs of alcohol poisoning?
Early symptoms include confusion, vomiting, seizures, slow or irregular breathing, and loss of consciousness.
How does alcohol poisoning differ from being drunk?
Intoxication may impair judgment and coordination, but alcohol poisoning is a medical emergency that compromises vital life support functions and can lead to severe complications.
Can alcohol poisoning be treated at home?
No, alcohol poisoning requires professional medical treatment. Attempting to treat it at home, especially by trying to induce vomiting or cool the person rapidly, can be very dangerous.
How long does it take to recover from alcohol poisoning?
Recovery time varies based on the amount of alcohol consumed and individual health factors. Hospitalization may be necessary for continuous monitoring and treatment.
Is alcohol poisoning common among first-time drinkers?
First-time drinkers, including teens and college-age individuals, are at higher risk because they often have lower tolerance levels and may not understand safe drinking practices.
Your Path to Recovery Starts Now With Lumina Recovery
Understanding alcohol poisoning, including its causes, symptoms, life-saving first aid steps, and recognizing early signs, is vital for timely intervention.
At Lumina Recovery, our comprehensive partial hospitalization program (PHP) and telehealth services are designed to support you from crisis management to long-term recovery, helping you avoid alcohol poisoning and regain control of your life.
Contact Lumina Recovery today for the guidance and support you need on your journey to a healthier life.

How Does Alcohol Affect the Stomach and Digestive System?
The effects of alcohol on the digestive system can lead to serious health issues. Alcohol can irritate the stomach lining, interfere with nutrient absorption in the intestines, and contribute to liver and pancreatic diseases.
Whether you struggle with heavy drinking or care for someone with a drinking problem, knowing these impacts is vital. Understanding how the amount of alcohol consumed affects the digestive tract, from immediate irritation to long-term complications, can help reduce the risk of developing severe conditions.
Overview of the Digestive System
The digestive system breaks down food and absorbs nutrients. It comprises key organs:
- Mouth: Chews food and mixes it with saliva
- Esophagus: Moves food to the stomach
- Stomach: Uses acids and enzymes to digest food
- Small Intestine: Absorbs nutrients
- Large Intestine: Absorbs water and forms waste
- Liver: Detoxifies substances and produces bile
- Pancreas: Creates digestive enzymes and hormones
- Gallbladder: Stores bile for fat digestion
Each part plays a role in keeping your body nourished, but alcohol can disrupt this balance.
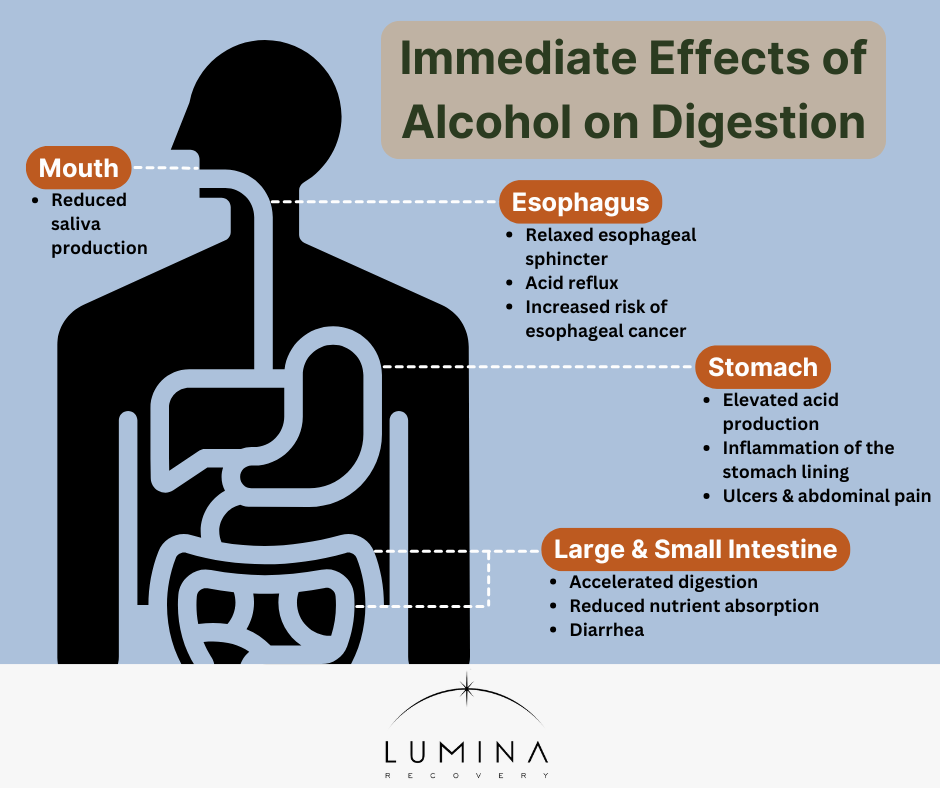
Immediate Effects of Alcohol on Digestion
Right after you consume alcohol, your body experiences immediate changes that can set the stage for further digestive problems.
Mouth and Esophagus
When you drink, alcohol immediately reduces saliva production in your mouth. It also relaxes the esophageal sphincter, the muscle that stops stomach acid from rising. This disruption can lead to acid reflux, which over time increases the risk of developing esophageal cancer.1
Stomach
In the stomach, alcohol increases acid production. This extra acid can cause inflammation of the stomach lining, leading to ulcers and abdominal pain.1 Alcohol-induced damage can compromise the stomach’s natural defenses, making it vulnerable to further injury.
Small and Large Intestine
Alcohol speeds up digestion in the small intestine, reducing nutrient absorption.2 The rapid transit through the digestive tract can also lead to diarrhea, as the large intestine does not have enough time to absorb water properly. Even one episode of excessive alcohol consumption can upset this balance.
Long-Term Effects of Chronic Alcohol Consumption
Over time, the cumulative impact of alcohol can create lasting changes in your body that severely compromise the digestive system.
Liver
Chronic heavy drinking is a major risk factor for liver disease. Repeated exposure to high amounts of alcohol increases the risk of developing conditions like fatty liver, hepatitis, and ultimately cirrhosis. Over the long term, such damage impairs the liver’s ability to detoxify the body.
Pancreas
The pancreas is also vulnerable. Prolonged drinking can trigger acute pancreatitis, a painful condition that inflames the pancreas and disrupts its function. Recurrent episodes may lead to lasting damage, complicating digestion and blood sugar regulation.
Increased Cancer Risks
Alcohol disrupts normal cell cycles, leading to chronic inflammation and damage to your DNA. When DNA is harmed, cells may begin to grow uncontrollably, and it increases the risk of developing various cancers. The presence of alcohol in the mouth also makes it easier for cells to absorb carcinogens, further raising the risk of developing cancer.3
Alcohol’s Impact on the Gut Microbiome
There is a strong relationship between gut health and alcohol addiction because alcohol alters the gut microbiome. This community of bacteria is essential for digestion and overall health. Excessive alcohol consumption can cause dysbiosis, where harmful bacteria outnumber the beneficial ones.4
This imbalance may lead to a “leaky gut,” potentially triggering systemic inflammation that can worsen digestive problems over time.4
5 Factors Influencing Alcohol’s Effects
Several factors shape how alcohol affects your digestive system and body:
- Type of beverage. Different drinks, whether beer, wine, or spirits, have unique properties that can influence the digestive system.
- Amount of alcohol. The more you drink, the greater the immediate and long-term effects of alcohol.
- Drinking patterns. Heavy drinking or binge drinking sharply increases the risk of digestive damage.
- Individual health. Pre-existing conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or celiac disease, can make the effects of alcohol even more severe.
- Duration. The long-term impact of regular alcohol use compounds over time, escalating the risk of serious health issues.
Understanding these factors can help you make smarter choices about your drinking habits.
Recognizing Symptoms of Alcohol-Related Digestive Issues
It’s important to spot the warning signs early. Common symptoms include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating and gas
- Changes in bowel habits
- Acid reflux
If these symptoms persist, seek medical advice promptly.

Treatment and Management of Alcohol-Induced Digestive Disorders
If you experience ongoing digestive issues related to alcohol, there are several treatment options available to help you regain control of your health.
Medical intervention may include the prescription of medications to manage symptoms such as abdominal pain and acid reflux. In severe cases, hospitalization might be necessary.
Alongside this, a balanced diet rich in vitamins and probiotics plays a vital role in restoring gut health, particularly in the small intestine. Lifestyle changes, including reducing or eliminating alcohol consumption, are crucial for long-term improvement, and counseling or support groups can provide guidance to help you develop healthier habits.
Regular monitoring with ongoing check-ups also ensures that any early signs of complications are promptly addressed, keeping you on track toward recovery.
FAQs
How does alcohol consumption lead to stomach ulcers?
Alcohol increases acid in the stomach, causing inflammation of the stomach lining that erodes its protective barrier, resulting in ulcers and abdominal pain.1
Can drinking alcohol cause diarrhea?
Yes. Alcohol speeds up digestion in the small intestine, reducing water absorption and causing diarrhea.1
Why do I experience acid reflux after drinking?
Alcohol relaxes the esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach acid to flow back, which can eventually lead to esophageal cancer.
Is nutrient absorption affected by alcohol?
Chronic alcohol consumption damages the lining of the digestive tract, impairing the absorption of essential nutrients.
How does alcohol consumption increase cancer risks?
The toxic byproducts from alcohol metabolism increase the risk of developing cancers in the digestive system, making alcohol a major risk factor.
Start a New Path to Wellness With Lumina Recovery
Alcohol can take a serious toll on the digestive system, causing immediate issues like acid reflux and abdominal pain to long-term conditions such as liver disease and acute pancreatitis. The amount of alcohol consumed, drinking patterns, and overall health all play a role in determining the severity of these effects.
At Lumina Recovery, our dual diagnosis treatment addresses addiction and co-occurring conditions like anxiety and depression, while our outpatient programs provide flexible support for those balancing recovery with daily responsibilities.
If you or a loved one faces these challenges, contact us today to start your journey toward lasting recovery.
Sources:
- UNC Health. 6 Ways Alcohol Can Damage Your Gut.
- Butts M, Sundaram VL, Murughiyan U, et al. The Influence of Alcohol Consumption on Intestinal Nutrient Absorption: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients. 2023 Mar 24;15(7):1571. doi: 10.3390/nu15071571.
- CDC. Alcohol and Cancer.
- Cleveland Clinic. Dysbiosis.

Does Having Alcohol Shakes Mean You’re an Alcoholic?
No, experiencing alcohol shakes does not automatically mean you are an alcoholic, but it can be a sign of alcohol dependence or withdrawal.
They occur when the nervous system reacts to alcohol leaving the body, and while they are common in heavy drinkers, they can also affect those who consume alcohol occasionally.
Understanding the causes of alcohol shakes can help determine whether they indicate a deeper issue related to alcohol dependence or another medical condition. We will explore what alcohol shakes are, their causes, and when they may be a sign of alcoholism.
What Are Alcohol Shakes?
Alcohol shakes, also known as alcohol tremors, are a form of tremor that results from the body’s nervous system being affected by alcohol consumption and withdrawal. They typically occur as a withdrawal symptom when a person stops drinking after prolonged or heavy use.
However, their severity can vary significantly, from mild shaking in occasional drinkers to severe, persistent tremors in those with chronic alcohol addiction.
Alcohol Shakes vs. Other Tremors
It’s important to differentiate alcohol-related tremors from other types of shakes:
- Anxiety-related tremors: Often temporary and triggered by stress.
- Essential tremors: A neurological condition that causes shaking without alcohol involvement.
- Parkinson’s disease tremors: A movement disorder that worsens over time and has distinct symptoms beyond tremors.
- Medication side effects: Some prescription drugs cause tremors as a side effect.
- Blood sugar imbalances: Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) can cause shaking, especially in diabetics.

Causes of Alcohol Shakes
Alcohol shakes can be distressing and are often a sign that the body is reacting to changes in alcohol consumption. Understanding what causes these tremors can help individuals determine whether they are experiencing withdrawal or another underlying issue.
1. Alcohol Withdrawal
When someone stops drinking after prolonged alcohol use, the nervous system, which has adapted to alcohol’s depressant effect, becomes overactive. This can cause the brain to send incorrect signals to the nerves, leading to involuntary shaking, particularly in the hands and fingers.1
These tremors typically occur within hours after the last drink and may persist until the body stabilizes.
2. Alcohol-Related Brain Damage
Long-term alcohol use can cause damage to the brain and nervous system, interfering with the way the brain communicates with muscles and nerves. This disruption can result in persistent tremors, even when a person is not actively withdrawing from alcohol.
These tremors may indicate underlying neurological impairment due to chronic alcohol consumption.1
Understanding the cause of alcohol shakes is essential in determining whether they are a
temporary withdrawal symptom or a sign of long-term alcohol-related damage.
Do Alcohol Shakes Indicate Alcoholism?
While alcohol shakes are commonly linked to withdrawal symptoms in individuals with alcohol dependence, they are not always a definitive symptom of alcoholism.
Many factors contribute to alcohol shakes, including excessive alcohol consumption, binge drinking, and the body’s reaction to stopping alcohol intake. The severity of tremors can vary from person to person, depending on their drinking patterns, overall health, and whether they have developed alcohol dependence.
For some, alcohol shakes may occur only after consuming large amounts of alcohol, while for others, they may be an early warning sign of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. In severe cases, alcohol tremors can be a symptom of delirium tremens (DTs), a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention.
It is important to understand that alcohol shakes are not exclusive to heavy drinking or those with long-term alcohol addiction. Seeking professional help can provide clarity and support for those unsure of what their symptoms mean.

How to Stop Alcohol Shakes Safely
If you or a loved one is experiencing alcohol-related tremors, taking the right steps is crucial.
Short-Term Relief
- Hydration: Drinking water can help restore balance.
- Nutrition: Eating nutrient-rich foods helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Rest: Getting proper sleep and reducing stress can minimize shakes.
When to Seek Medical Help
Alcohol withdrawal can be dangerous. Seek professional help if you have the following signs of alcohol withdrawal:1
- Severe tremors lasting more than 48 hours after the last drink
- Confusion, hallucinations, or seizures
- Rapid heart rate
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Severe nausea and vomiting
- Sudden mood changes, including depression and anxiety
- Sweating and persistent headaches
- Difficulties sleeping or insomnia
Long-Term Solutions
If alcohol shakes are a recurring problem, professional treatment can help:
- Medically Supervised Detox: Provides a safe environment for withdrawal management.
- Inpatient or Outpatient Treatment: Offers therapy and medical support for recovery.
- Therapy: Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and medication-assisted treatment (MAT) help address the underlying causes of alcohol dependence.
FAQs
Can alcohol shakes be a sign of something other than withdrawal?
Yes. While alcohol shakes are commonly associated with withdrawal, they can also be caused by anxiety, neurological disorders, medication side effects, and low blood sugar levels. If tremors persist, it is important to consult a medical professional to determine the underlying cause.
How long do alcohol shakes last?
Alcohol shakes usually last between a few hours to a couple of days, depending on the severity of withdrawal.
Can alcohol shakes be permanent?
In most cases, alcohol shakes subside with detox. However, long-term alcohol use can cause nerve damage, leading to persistent tremors.
Do all heavy drinkers get shakes?
Not necessarily. Some individuals are more prone to withdrawal symptoms, while others may not experience noticeable tremors.
What is the fastest way to stop alcohol shakes?
Hydration, proper nutrition, and rest can help, but if symptoms are severe, medical supervision is the safest option.
Find Stability and Support With Lumina Recovery
Alcohol shakes can be a warning sign of withdrawal, but they don’t necessarily mean someone is an alcoholic. If tremors persist or are accompanied by other withdrawal symptoms, seeking professional guidance is crucial.
At Lumina Recovery, we offer medically supervised detox and individual therapy to help manage alcohol dependency safely.
If you or a loved one is experiencing withdrawal symptoms, contact Lumina Recovery today for a confidential consultation.
Source:
- Medical News Today. Understanding alcohol “shakes” and tremors.

What Is Blacking Out? Definition and Dangers of Getting Blackout Drunk
Blacking out from alcohol occurs when excessive drinking prevents the brain from forming new memories, leading to gaps in recall. Unlike passing out, a person in a blackout remains conscious but has no recollection of events.
Alcohol-induced blackouts are common among college students and young adults, particularly those who engage in binge drinking or consume large amounts of alcohol quickly. Understanding the causes, risks, and long-term effects of blackouts can help prevent dangerous behaviors and alcohol-related harm.

What Are Alcohol-Induced Blackouts?
Blacking out occurs when alcohol interferes with the brain’s ability to store long-term memories. The hippocampus, the region responsible for memory formation, is particularly affected by alcohol, which prevents the encoding of new information.1 As a result, a person may spend an entire night drinking and socializing, yet wake up with no memory of what happened.
There are two types of blackouts, classified based on the severity of memory loss:
- An en bloc blackout, also called a complete blackout, causes total amnesia for the duration of intoxication. A person experiencing this form of blackout will be unable to recall events, no matter how many reminders they are given. The memories were never stored, making it impossible to retrieve them.
- A fragmentary blackout, sometimes called a brownout, is a partial memory loss where bits and pieces of the night may come back when prompted. This type of blackout is more common and often not recognized until someone else fills in the gaps the next day.1
Causes and Risk Factors for Blackouts
According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, alcohol-induced blackouts can occur when blood alcohol concentrations (BACs) reach 0.16% or higher, nearly twice the binge drinking threshold of 0.08%.1
At this level, the brain struggles to form new memories, and key cognitive functions like judgment, impulse control, and decision-making become severely impaired. This makes blackouts especially dangerous, increasing the risk of accidents, risky behaviors, and alcohol poisoning.
How Blackouts Happen
Several factors can increase the risk for blackouts, including:
- Rapid drinking – When alcohol is consumed too quickly, BACs rise at an accelerated rate, preventing the brain from storing memories.
- Drinks on an empty stomach – Without food to slow alcohol consumption, BACs spike faster, making blackouts more likely.
- Mixing alcohol with medications – Certain drugs, especially sleep aids and anti-anxiety medications, can make blackouts happen at much lower BACs.
- Binge drinking – Drinking large amounts of alcohol in a short period can quickly push BACs into blackout territory.
Women are generally more prone to blackouts than men because of physiological differences in alcohol metabolism. Genetics can play a role, as some people are more predisposed to experiencing blackouts based on how their bodies process alcohol.
The Dangers of Alcohol-Induced Blackouts
Blackouts pose both immediate and long-term dangers. In the short term, a person experiencing a blackout may engage in risky behaviors without realizing it. Actions such as drunk driving, unprotected sex, vandalism, or aggressive behavior can have serious consequences, yet the person may have no recollection of making those choices.
Repeatedly drinking to the point of blackout increases the risk of developing a dependence on alcohol. Over time, heavy alcohol consumption can lead to permanent cognitive impairments, making it more difficult for the brain to retain new information.
In addition to its impact on memory formation, chronic alcohol use can contribute to neurological damage. People who regularly experience blackouts and damage their frontal lobe may suffer long-term changes in brain function, particularly affecting long-term memory, personality, and decision-making abilities.2

When to Seek Help for Alcohol-Related Issues
Experiencing a single blackout may not necessarily indicate a drinking problem, but frequent blackouts are a red flag for alcohol abuse and alcoholism. If blackouts become a regular occurrence, it may be time to evaluate drinking habits and seek support.
Some signs that indicate problematic drinking include:
- Drinking despite negative consequences
- Feeling unable to control alcohol intake
- Using alcohol as a coping mechanism for stress, anxiety, or depression
For individuals struggling with frequent blackouts, professional help is available. Detox programs provide a safe, supervised environment for managing alcohol withdrawal, while outpatient treatment programs offer therapy and support for long-term recovery.
Addressing the root causes of excessive drinking can help break the cycle of blackouts and prevent lasting damage to brain function.
FAQs
What is the difference between blacking out and passing out?
Blacking out refers to memory loss during intoxication while remaining conscious. A person can still interact with others but will not remember those moments. Passing out, on the other hand, means losing consciousness entirely due to excessive alcohol consumption.
Can blacking out from alcohol cause permanent brain damage?
Frequent blackouts can contribute to cognitive decline, memory impairment, and an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases. While one blackout may not cause lasting damage, repeated episodes can negatively impact brain function.
How can I tell if I’m about to blackout?
Warning signs of an impending blackout include difficulty remembering recent conversations, slurred speech, impaired coordination, and an inability to focus. If these symptoms appear, stopping alcohol consumption is advised.
Are some people more prone to blacking out than others?
Yes. Genetics, gender differences (women typically experience blackouts more easily), and drinking patterns all affect a person’s susceptibility. Binge drinking and consuming large amounts of alcohol in a short time also increases blackout risk.
What should I do if someone blacks out from drinking?
If someone is experiencing a blackout, ensure their safety by staying with them and keeping them hydrated. If they become unresponsive or show signs of alcohol poisoning, seek medical help immediately.
Protect Your Health and Well-Being With Lumina Recovery
Alcohol-induced blackouts can have dangerous consequences, from impaired decision-making to long-term cognitive damage. Recognizing the risks and taking proactive steps to prevent blackouts can lead to safer drinking habits and a healthier lifestyle.
For those struggling with frequent blackouts or signs of alcohol abuse and alcoholism, Lumina Recovery offers comprehensive detox, inpatient treatment programs, and outpatient treatment programs to help individuals regain control of their lives from alcohol abuse.
Contact us today to take the first step toward a sober, healthier future.
Sources:
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Interrupted Memories: Alcohol-Induced Blackouts.
- Healthline. Understanding Why Blackouts Happen.

Perfectionism in Addiction Recovery
Perfectionism is the tendency to set unrealistically high standards for oneself, often accompanied by harsh self-criticism when these standards are not met. Many individuals who struggle with addiction also exhibit perfectionistic traits, either before their substance use begins or as part of their recovery journey.
While striving for excellence can be a positive trait, perfectionism can contribute to stress, anxiety, and self-doubt, which may, in turn, influence both addiction and recovery processes. Recognizing the connection between perfectionism and addiction is crucial in developing a sustainable recovery plan.
What Is Perfectionism?
Perfectionism is the belief that anything short of flawlessness is unacceptable. It’s a complex psychological trait that can influence multiple aspects of a person’s life, including their self-worth, relationships, and ability to cope with challenges.
3 Types of Perfectionism
There are three main types of perfectionism, each with distinct characteristics:
- Self-Oriented Perfectionism: Imposing excessively high expectations on oneself, often leading to self-criticism and disappointment. This can include moral perfectionism, where individuals feel intense guilt or shame when they fall short of their own rigid ethical or moral standards.
- Socially Prescribed Perfectionism: The belief that others expect perfection, resulting in fear of judgment or failure. This form of perfectionism can create intense pressure to meet external standards, leading to anxiety, stress, and self-doubt.
- Other-Oriented Perfectionism: Holding others to unattainable standards, leading to frustration and strained relationships. This type of perfectionism can create tension in both personal and professional relationships, as those affected may struggle with disappointment when others do not meet their high expectations.
Psychological Impacts
Perfectionism can significantly impact mental health, increasing the risk of:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Low self-esteem
- Feelings of inadequacy and shame
- Difficulty in accepting mistakes or setbacks

The Link Between Perfectionism and Addiction
The relentless pursuit of flawlessness can create immense emotional distress. Individuals who feel they can never meet their own or others’ expectations may turn to substances as a way to numb their stress, anxiety, or feelings of failure:
- Emotional avoidance. Perfectionists may use substances to escape overwhelming emotions like shame or inadequacy.
- Fear of judgment. The constant worry of failing in front of others can drive individuals toward substance use as a coping mechanism.
- Inability to tolerate mistakes. Perfectionists may feel that even minor missteps are unacceptable, leading to a cycle of self-punishment and addiction.
Perfectionists often experience black-and-white thinking, viewing themselves as either completely successful or entirely failing. When they feel they cannot meet their high expectations, they may use substances to escape the emotional burden of their perceived shortcomings.
The Vicious Cycle
Once addiction takes hold, perfectionism can make recovery even more challenging. The pressure to maintain unrealistic standards can create overwhelming feelings of guilt and shame, reinforcing the cycle of addiction as individuals turn to substances for escape. Here are some key ways in which perfectionism can negatively impact the recovery process:
- Increased self-criticism. A relapse or setback can trigger harsh self-judgment, further deepening the cycle of addiction.
- Struggle with acceptance. Perfectionists may find it difficult to accept the imperfection of recovery, leading to frustration and discouragement.
- Risk of relapse. If progress isn’t perceived as perfect, some may experience overwhelming guilt, making them more vulnerable to relapse.
Perfectionism During Recovery
Recovery is not a linear process, but perfectionists may struggle to accept setbacks. Common challenges include:
- Fear of failure. Worrying that any mistake or lapse means complete failure.
- Believing one can control recovery alone, leading to risky behaviors.
- Unrealistic expectations. Expecting immediate or flawless progress and becoming discouraged when setbacks occur.
- Moral perfectionism in recovery. Feeling overwhelming guilt for past mistakes and struggling to forgive oneself, which may hinder emotional growth and progress.
Because perfectionists often struggle with self-acceptance, they may experience overwhelming guilt or frustration when recovery is not perfect, increasing the risk of relapse.

Strategies to Manage Perfectionism in Recovery
Overcoming perfectionism in recovery requires a combination of self-awareness, intentional habit changes, and emotional resilience. One of the most effective approaches is cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), which helps individuals recognize and challenge perfectionistic thought patterns.
Setting realistic goals is another key strategy. Rather than expecting immediate success, focusing on small, attainable milestones can encourage steady progress. Acknowledging achievements, no matter how minor, can foster motivation and reinforce a positive mindset.
Practicing self-compassion and mindfulness is essential in breaking free from the cycle of perfectionism. Techniques such as meditation, journaling, and positive affirmations help individuals cultivate self-acceptance. Accepting mistakes as learning opportunities rather than failures allows for a more balanced and resilient approach to recovery.
Finally, seeking support from a community plays a crucial role in managing perfectionism. Seeking therapy, joining support groups, and openly communicating with loved ones can provide essential encouragement and accountability.
Working with professionals specializing in addiction and perfectionism recovery can further equip individuals with the tools needed for lasting change.
FAQs
What is the connection between perfectionism and addiction?
Perfectionism can lead to unrealistic self-expectations, causing stress and emotional distress. Individuals may turn to substances as a coping mechanism to manage these feelings.
How does perfectionism affect the recovery process?
Perfectionistic tendencies during recovery can lead to fear of failure and unrealistic expectations, potentially increasing the risk of relapse if progress isn’t perceived as perfect.
Can perfectionism be treated alongside addiction?
Yes, addressing perfectionism is crucial in addiction treatment. Therapies like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals recognize and modify perfectionistic thought patterns.
How to overcome perfectionism while in recovery?
Overcoming perfectionism involves practicing self-compassion, setting realistic goals, seeking therapy, and engaging in mindfulness practices to reduce self-judgment.
Find Help for Perfectionism and Addiction With Lumina Recovery
Perfectionism can be a significant obstacle in addiction recovery, but it doesn’t have to define your journey. By acknowledging that setbacks are part of the process, practicing self-compassion, and seeking support, individuals can build a more sustainable path to healing.
At Lumina Recovery, we offer cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and dual diagnosis programs designed to help individuals manage perfectionistic tendencies while overcoming addiction.
If you or a loved one is struggling, contact us today to start the journey toward recovery.

How Long Does Meth Stay in Your System?
Meth can stay in your system for anywhere from 24 hours to 90 days. The type of drug test used will affect how long after use it can be detected, but the actual time it stays in your system depends on several factors like your metabolism, frequency of use, and overall health.
Meth is a highly addictive stimulant that affects the central nervous system by creating a flood of dopamine. However, this rush comes with severe health consequences and a high risk of addiction.
Understanding how long meth stays in your system is crucial for those in recovery from meth addiction, individuals undergoing workplace or legal testing, and loved ones concerned about meth use.
What Is Methamphetamine?
Methamphetamine, commonly called meth, is a synthetic stimulant that is illegal in most forms except for specific medical uses under prescription. It comes in different forms, such as powder, crystals (crystal meth), and pills.
Meth use produces short-term effects such as increased energy, alertness, and a suppressed appetite. Chronic use leads to long-term damage, including cognitive impairments and severe physical health problems.1
How Methamphetamine Is Metabolized
When meth is consumed, it enters the bloodstream rapidly, affecting the brain and body within minutes. The liver primarily metabolizes it into amphetamine and other byproducts, which are excreted through urine.
The factors that influence how long meth stays in your system include:
- Metabolism Rate – Faster metabolisms clear meth more quickly.
- Age and Health – Older individuals and those with liver or kidney issues may take longer to process meth.
- Frequency of Use – Chronic users retain meth longer in their system.
- Hydration and pH Levels – More acidic urine helps eliminate meth faster.
Detection Windows by Testing Method
The amount of time meth stays in your system depends on the type of drug test used. Each method has different detection windows based on how meth is metabolized in the body.
Urine Tests
Urine testing is the most common method for detecting methamphetamine use. Meth stays in urine for as long as 72 hours after use, though in chronic users, it may be detectable for four or more days.1 Factors such as hydration levels and metabolism can influence the detection window.
Blood Tests
Blood tests detect methamphetamine shortly after use but have a relatively brief detection window. Due to this short timeframe, blood tests are less commonly used for routine screening and are more often employed in emergency situations or to determine current impairment.
Saliva Tests
Saliva tests are another way to detect meth use, with a detection window of approximately 48 hours after last use.2 Saliva tests are used in workplace screenings and roadside drug tests due to their convenience.
Hair Follicle Tests
Hair follicle tests may identify meth up until 90 days following use. These tests provide a long-term overview of substance use history but are less effective for detecting recent use. Studies suggest that approximately 16% of individuals who chronically use meth may still have detectable amounts in their hair after 120 days.1

Factors That Influence How Long Meth Stays in Your System
How long meth stays in the body depends on several factors, including:
- Method of Use – Smoking and injecting meth result in quicker highs and faster elimination, while oral consumption extends the drug’s presence in the system.
- Frequency and Dosage – Heavy users will have meth stored in fat cells, prolonging its presence.
- Hydration and Diet – Dehydration can slow down meth elimination.
Methamphetamine Half-Life
Meth has a half-life of 6 to 15 hours, meaning half of the drug can be metabolized within this period.3 However, traces of meth and its byproducts can remain in the system for days, influencing detection times.
Risks of Attempting to Alter Detection Times
Many people try to clear meth from their systems using detox kits or other methods, but this can be dangerous. Rapid detoxing can cause dehydration, heart complications, and severe withdrawal symptoms. Additionally, tampering with drug tests may lead to legal consequences.
The Effects of Meth and Long-Term Risks
The effects of meth extend beyond its stimulating high. Long-term use can cause:1
- Severe dental decay
- Extreme weight loss
- Meth sores
- Memory loss
- Psychosis
Chronic meth use can cause irreversible damage to dopamine receptors, leading to an inability to feel pleasure naturally. This significantly contributes to addiction and mental health struggles.

Importance of Seeking Professional Help
Detox from meth can be challenging, but medical professionals can help manage withdrawal symptoms safely. Professional treatment programs provide comprehensive care, including:
- Medically supervised detox to help clear the drug from your system safely.
- Inpatient and outpatient treatment programs that offer structured support.
- Behavioral therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), help individuals develop healthy coping mechanisms.
FAQs
How long does meth stay in your urine?
Meth can be detected in urine tests until 72 hours after use, though chronic use can extend this period to a week.
Can meth be detected in a hair follicle test?
Yes, meth can be detected in hair follicle tests up until 90 days post-use.
What factors affect how long meth stays in your system?
Factors include frequency of use, metabolism, hydration levels, urinary pH, and overall well-being.
Your Path to Recovery Starts With Lumina Recovery
Methamphetamine can have devastating consequences, but recovery is possible with the right support. Understanding how long meth stays in your system is just one step toward regaining control of your life. If you or someone you care about is facing challenges with meth use, getting professional support is essential.
At Lumina Recovery, we offer detox programs to safely clear meth from your system and meth addiction treatment programs that provide long-term support. Whether you need inpatient care or outpatient support, our experienced medical professionals are here to help.
Take the first step toward a healthier future. Contact Lumina Recovery today.
Sources:
- Healthline. How Long Does Meth Stay in Your Urine?
- Alcohol and Drug Foundation. Roadside drug testing.
- Richards JR, Laurin EG. Methamphetamine Toxicity. [Updated 2023 Jun 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan.

What Is a “Beer Gut”?
A beer gut, also known as a beer belly, is the common term that describes excess fat accumulating around the abdomen, often linked to frequent beer consumption. While beer is commonly blamed for this condition, the underlying causes are more complex.
Alcohol addiction and excessive drinking can contribute significantly to weight gain, but other lifestyle factors, such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and genetics, can also play a role.
Understanding the connection between alcohol consumption, addiction, and belly fat accumulation is essential to addressing the issue effectively.
What Is Abdominal Fat?
A growing waist size, particularly when it exceeds 40 inches in men or 35 inches in women, signals a potential health risk.1 Not all belly fat is the same, and understanding these two types is crucial for addressing the issue effectively.
- Subcutaneous fat lies just beneath the skin and is generally less harmful. It contributes to overall body fat but does not pose significant health risks.
- Visceral fat accumulates around internal organs and can lead to serious health complications. It increases the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other health problems.1
Causes of a Beer Gut
A beer gut is often associated with long-term alcohol consumption, which leads to excessive calorie intake, metabolic changes, and lifestyle disruptions. Individuals who struggle with alcohol dependence often consume high-calorie drinks frequently, leading to an increased risk of fat accumulation, particularly around the abdomen.
Caloric Intake and Weight Gain
Beer is often associated with belly fat because of its caloric density. A typical beer contains about 150 calories, and excessive consumption can lead to weight gain over time.2 If these calories are not burned through physical activity, they contribute to fat accumulating in the abdominal region.
Alcohol’s Role in Fat Storage
The body prioritizes metabolizing alcohol over burning fat, which can slow down weight loss efforts. Additionally, alcohol increases appetite and lowers inhibitions, making it easier to overeat unhealthy foods. This combination can cause excess body fat, particularly around the midsection.
Sedentary Lifestyle and Poor Diet
A lack of physical activity allows fat to accumulate unchecked. Many individuals with a beer belly consume diets high in processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats, further contributing to abdominal weight gain. Without regular exercise and a balanced diet, reducing waist size becomes challenging.
Genetic and Hormonal Influences
Some individuals are predisposed to storing fat in the abdominal region due to genetics. Chronic alcohol consumption can alter hormone levels, making it easier to gain weight and harder to lose weight.

3 Health Risks of a Beer Gut
Alcohol addiction puts those at an increased risk of developing a beer gut, and the health risks associated with it go beyond appearance. Over time, this accumulation of visceral fat contributes to serious health conditions.
1. Cardiovascular Disease
Carrying excess visceral fat poses a higher risk for heart disease and high blood pressure. The accumulation of fat in the abdominal region correlates with higher cholesterol levels and arterial inflammation, which contribute to the risk of heart complications.2
2. Metabolic Disorders and Type 2 Diabetes
An expanding beer belly is often linked to type 2 diabetes, as excess visceral fat can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar. Over time, this can increase the chances of developing diabetes and related health risks, such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision loss.
3. Fatty Liver Disease
Other health problems like fatty liver disease are often linked to excess alcohol consumption and the accumulation of abdominal fat. When the liver stores too much fat, it can lead to inflammation, liver damage, and long-term health complications.
Understanding the link between alcohol addiction and health risks is essential for those looking to make lasting changes to their health and well-being
How to Get Rid of a Beer Gut
Since alcohol addiction can play a role in developing a beer gut, addressing the root dependency is crucial for long-term health. Overcoming addiction requires a structured approach that includes professional treatment, lifestyle changes, and healthier habits.
Addiction Treatment and Recovery
- Seek professional help through outpatient programs, supervised detox, or group therapy to manage alcohol dependency.
- Address co-occurring mental health issues that may contribute to excessive drinking and weight gain.
- Participate in dual diagnosis treatment to address both addiction and underlying emotional triggers.
Healthy Dietary Adjustments
- Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Reduce 150 calories per day to gradually decrease fat accumulation.
- Avoid sugary beverages and processed foods to prevent excess belly fat.
- Increase fiber intake to promote fullness and regulate blood sugar levels.
Exercise Strategies for Belly Fat Reduction
- Participate in aerobic activities such as jogging, biking, or swimming to help expend energy.
- Include resistance exercises to enhance muscle development and support metabolic function.
- Combine different types of workouts for long-term fat loss.
- Try high-intensity interval training (HIIT) for effective visceral fat
Manage Stress and Sleep Quality
- Practice mindfulness, meditation, or yoga to lower stress levels.
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule to regulate hormone levels.
- Reduce chronic stress to lower cortisol levels and minimize belly fat
- Engage in relaxation techniques to enhance overall well-being.
By addressing alcohol addiction alongside lifestyle changes, individuals can achieve sustainable weight loss and improve overall health.

FAQs
What causes a beer gut?
A beer gut is caused by excessive calorie intake, particularly from alcohol, which contributes to weight gain and fat accumulation around the abdomen. Alcohol slows fat metabolism, and beer, being high in calories and carbs, can lead to increased visceral fat storage.
How long does it take to lose a beer belly?
With consistent dietary and exercise efforts, noticeable changes can occur within 8 to 12 weeks. However, individual results vary based on metabolism and lifestyle choices.
What is considered a beer gut?
A beer gut refers to the accumulation of excess belly fat, often protruding outward, typically associated with frequent alcohol consumption, especially beer. It results from the storage of visceral fat around the abdominal organs, giving the midsection a rounded appearance.
Take Control of Your Health With Lumina Recovery
A beer gut signals potential health risks, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and other health problems. While beer consumption plays a role, factors such as diet, physical activity, and genetics contribute significantly to belly fat. Reducing waist size and improving overall health requires a balanced approach.
If alcohol is affecting your ability to lose weight and maintain a healthy lifestyle, Lumina Recovery’s alcohol addiction programs offer structured support for reducing dependence. Additionally, our dual diagnosis treatment addresses underlying factors like stress and anxiety that contribute to unhealthy habits.
If you’re ready to make a lasting change, contact Lumina Recovery today.
Sources:
- Cleveland Clinic. Does Beer Really Cause a ‘Beer Belly’?.
- WebMD. The Truth About Beer and Your Belly.
Additional Resources
Once you have completed your rehabilitation program at one of our drug and alcohol treatment centers, you should try to surround yourself with people who can encourage you to stay sober. Many people find that support groups are the best source of encouragement. You can find hundreds of support groups and meetings in your community. Our drug addiction treatment centers stress the importance of personal chemical dependency resources, especially when you are new to sobriety. Below are various addiction and mental health resources for people in recovery who want additional support.
Christian Addiction Recovery Resources
Our substance abuse services aren’t limited to specific programs, but rather we believe in the importance of incorporating faith-based programs to promote spiritual healing, like our Faith in Recovery program.
With that said, below are some faith-based addiction recovery resources that could help you in your spiritual healing from addiction:
- Battlefield of the Mind by Joyce Meyer
- Boundaries by Dr. Henry Cloud & Dr. John Townsend
- Christian Families in Recovery: A Guide for Addiction, Recovery, and Intervention Using God’s Tools of Redemption by Robert and Stephanie Tucker
- Club New Life Christian Ministry for Addiction and Recovery
- Lost & Found: Recovery in Christ by Bruce Stanley
- Overcoming Emotional Obstacles through Faith: Navigating the Mind Field by Anthony Acampora, Director of Banyan’s Faith in Recovery Program
- The Case for Christ by Lee Strobel
Mental Health Resources for Recovery
Lumina Recovery consist of both mental health and substance abuse treatment facilities, meaning we offer mental health resources as well as chemical dependency resources. What’s more, addiction often co-occurs with mental illness, making these resources ever more important.
Below are some resources for mental health recovery that can help you or your loved one:
- This Emotional Life video series
- No Kidding, Me 2!! with Joe Pantoliano
- Dare: The New Way to End Anxiety and Stop Panic Attacks by Barry McDonagh
- Pleasure Unwoven: An Explanation of the Brain Disease of Addiction by Kevin McCauley
- Declutter Your Mind: How to Stop Worrying, Relieve Anxiety, and Eliminate Negative Thinking by S.J. Scott and Barrie Davenport
Call Us Today – (877) 716-7515

