
Our Addiction Resources
Navigating the world of addiction and recovery can be overwhelming. We’re here to provide clear, compassionate education and guidance. From practical advice for maintaining sobriety to informational guidance on the long-term effects of substance abuse, our content is a beacon of hope and understanding.
Our Team is Ready are ready to take your call
Call us Today!
or we can call you. Fill out form below
Our Blog

What Is the Definition of Alcoholism?
The definition of alcoholism, also known as alcohol use disorder (AUD), is a chronic disease that affects millions worldwide, impacting physical health, mental well-being, and relationships. According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), nearly 28.9 million people in the U.S. had an AUD in the last year.1
Alcoholism is a complex issue that affects not only individuals but also families and communities. From understanding the medical definitions to recognizing alcoholism’s impact on mental health, relationships, and society, we aim to provide valuable insights.

How Is Alcoholism Defined?
Alcoholism is defined as a chronic brain disorder that leads to compulsive alcohol consumption, loss of control over drinking, and withdrawal symptoms when alcohol use is reduced.
The NIAAA classifies alcohol use disorder as a medical condition that ranges from mild to severe based on diagnostic criteria. Unlike casual drinking, what constitutes alcoholism is its impact on both brain function and behavior, leading to a destructive cycle of dependence.2
What is considered alcoholism varies from person to person, but the stages of alcoholism and common indicators include excessive drinking, continued alcohol use despite adverse consequences, and strong cravings. Some people may develop alcoholism gradually, starting with occasional binge drinking before becoming physically dependent.
Signs and Symptoms of Alcoholism
What is alcoholism? Recognizing alcoholism involves identifying behavioral, physical, and mental symptoms that indicate dependency:3
Behavioral Symptoms
- Drinking more or longer than intended
- Neglecting responsibilities at work, school, or home
- Social withdrawal and increased secrecy about drinking
- Drinking in situations where it is dangerous, such as driving
- Continuing to drink despite interpersonal conflicts or strained relationships
Physical Symptoms
- Withdrawal symptoms like shaking, sweating, or nausea
- Increased tolerance requires more alcohol for the same effect
- Blackouts or memory loss
- Fluctuations in weight due to changes in appetite
- Frequent hangovers that impact daily functioning
Mental Symptoms
- Anxiety and depression linked to alcohol use
- Increased impulsivity and risk-taking behavior
- Mood swings and irritability
- Feeling guilty or ashamed about drinking habits
- Using alcohol as a way to cope with stress, sadness, or trauma
Health Risks and Consequences
Alcohol abuse can have both immediate and long-term effects on the body and mind, leading to severe health complications if left untreated:3
Short-Term Effects
- Impaired judgment leading to accidents and injuries
- Alcohol poisoning, which can be life-threatening
- Increased risk of violence and risky behaviors
- Slurred speech and lack of coordination
- Weakened immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections
Long-Term Effects
- Liver disease (cirrhosis, fatty liver disease)
- Cardiovascular problems, including high blood pressure and stroke
- Increased risk of mental health disorders like depression and anxiety
- Damage to the digestive system, leading to ulcers and malnutrition
- Decline in cognitive function, including memory loss and difficulty concentrating
- Increased risk of cancers including throat, mouth, breast, colon, and liver
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of alcoholism is essential in identifying those at higher risk and finding effective prevention and treatment strategies:
Genetics & Family History
- Studies suggest 50-60% of alcoholism cases have a genetic component4
- Having a close family member with AUD increases the risk
- Genetic predisposition combined with environmental factors can accelerate alcohol dependence
Environmental Factors
- Social norms and peer pressure surrounding alcohol use
- Childhood trauma, abuse, or neglect
- Stressful work environments or high-pressure careers
- Easy access to alcohol in social or cultural settings
Psychological Factors
- Stress and chronic anxiety
- Co-occurring mental health disorders like bipolar disorder or PTSD
- Low self-esteem and self-medicating with alcohol
How Is Alcoholism Diagnosed?
Determining whether someone has alcoholism involves assessing behavioral patterns, physical dependence, and psychological factors to ensure proper treatment.
DSM-5 Criteria for AUD
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) provides a framework for identifying alcohol-related conditions, with alcoholism defined as a disorder that meets at least two of the following criteria within a year:5
- Consuming more alcohol than originally planned.
- Unsuccessful efforts to reduce alcohol intake.
- Devoting a significant amount of time to obtaining, using, or recovering from alcohol.
- Failing to meet crucial obligations at work, school, or home due to alcohol consumption.
- Feeling a strong urge or compulsion to drink when not consuming alcohol.
- Continuing alcohol use even when it causes conflicts in personal relationships.
- Cutting back or completely abandoning social, professional, or leisure activities because of alcohol use.
- Engaging in dangerous behaviors, such as driving under the influence.
- Persisting in alcohol consumption despite known physical or psychological health issues.
- Needing to drink more alcohol over time to achieve the same effects.
- Experiencing physical or mental withdrawal symptoms when alcohol use is reduced or stopped.

Treatment and Recovery Options
There are a variety of treatment options for those with alcoholism. From rehab to therapy, there are many programs to suit your individual needs.
Detox and Rehabilitation Programs
Detox and rehabilitation programs are essential for individuals seeking to overcome alcoholism. Medically supervised detox helps manage withdrawal symptoms safely, ensuring a more comfortable transition to sobriety.
Residential inpatient programs offer structured recovery environments, providing continuous support and therapy. For those with work or family responsibilities, outpatient treatment programs offer flexible recovery options without requiring a stay at a treatment facility.
Therapy
Therapy plays a crucial role in treating alcoholism. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) helps individuals identify and change thought patterns that contribute to drinking behaviors. Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) provides strategies for managing emotions and reducing harmful behaviors related to alcohol use.
Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) is particularly effective for those whose alcohol use is linked to trauma. Individual therapy offers personalized support, helping clients explore the root causes of their addiction. Family therapy can also be beneficial, as it helps rebuild relationships affected by alcohol use and fosters a supportive home environment.
Support Groups
Support groups provide ongoing encouragement and community for those in recovery. Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) offers peer support through the well-known 12-step program, fostering accountability, and shared experiences.
SMART Recovery provides a science-based approach, focusing on self-empowerment and evidence-based techniques. Online support groups are also available, offering flexible ways for individuals to connect with others on the same journey toward sobriety.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the best definition of alcoholism?
Alcoholism, or alcohol use disorder (AUD), is a long-term mental illness that impairs a person’s ability to regulate their drinking, even when it leads to harmful outcomes. This disorder often includes physical reliance on alcohol, persistent cravings, increased tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms.
What is the legal definition of alcoholism?
The legal definition of alcoholism varies by jurisdiction but generally refers to a medical condition in which a person’s excessive alcohol use impairs their ability to function.
What is technically considered alcoholism?
Technically, alcoholism is considered a disorder when an individual meets the criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) for alcohol use disorder.
Get Help for Alcoholism With Lumina Recovery
Understanding what alcoholism is and how it is defined is the first step toward change. At Lumina Recovery, we offer personalized treatment plans that include medically supervised detox, inpatient rehab, therapy, and dual diagnosis treatment for co-occurring mental health conditions.
If you or a loved one is struggling with alcoholism, reach out to Lumina Recovery today to take the first step toward a healthier future.
Sources:
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) in the United States: Age Groups and Demographic Characteristics.
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Understanding Alcohol Use Disorder.
- Mayo Clinic. Alcohol use disorder.
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Risk Factors: Varied Vulnerability to Alcohol-Related Harm.
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Alcohol Use Disorder: From Risk to Diagnosis to Recovery.

How Long Does Alcohol Withdrawal Last?
Alcohol withdrawal occurs when someone who is dependent on alcohol suddenly stops drinking. Many people wonder, “How long is alcohol withdrawal?” as the timeline varies based on individual factors. This happens because the body has adapted to the presence of alcohol and struggles to function without it.
Knowing the answer to “How long does alcohol withdrawal take?” is crucial for a safe recovery. The process can vary depending on individual factors, but understanding what to expect can help in planning for a successful detox.
What Is Alcohol Withdrawal?
Alcohol withdrawal refers to a range of symptoms that emerge when an individual who has consumed large amounts of alcohol regularly suddenly decreases or ceases their intake. The body becomes physically dependent on alcohol over time, and when it is removed, the nervous system reacts, leading to withdrawal symptoms.
These symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe and life-threatening conditions, making it crucial to approach withdrawal with caution and medical guidance.
Several factors influence the severity of alcohol withdrawal, including:
- The duration and amount of alcohol consumption
- Individual health conditions, such as liver function and overall wellness
- Mental health disorders, such as anxiety or depression
- Whether the person has experienced withdrawal before
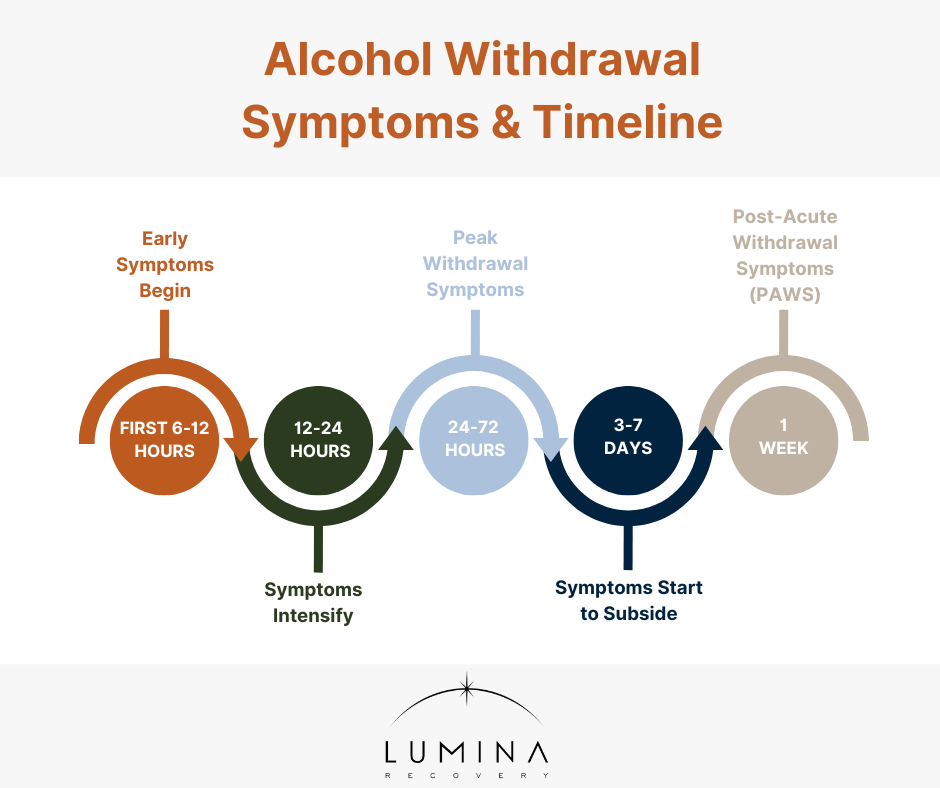
Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms and Timeline
The alcohol withdrawal time frame varies, but most people experience alcohol withdrawal symptoms day by day in predictable stages:1
- Within 6–12 hours post-consumption, individuals may experience loss of appetite, irritability, nausea, nervousness, restlessness, and pale skin.
- Between 12–24 hours after the last drink, some individuals may begin to experience mood swings, depression, nightmares, headaches, insomnia, and vomiting.
- During the 24–72 hour peak symptom period, withdrawal can cause hallucinations, nausea, and agitation. After 48 hours no alcohol, symptoms may worsen, with a high risk of seizures and delirium tremens (DTs). By 72 hours without alcohol, the most severe withdrawal symptoms typically reach their peak.
- Between 3–7 days, symptoms start to subside, though some individuals may continue experiencing persistent anxiety and insomnia. Individuals should talk to a healthcare provider if they are still experiencing symptoms.
- Beyond a week, some individuals may develop post-acute withdrawal syndrome (PAWS), characterized by anxiety, fatigue, and alcohol cravings that can persist for weeks or months.
4 Factors That Affect Withdrawal Duration
The duration and severity of alcohol withdrawal vary from person to person. Some key factors that influence the alcohol withdrawal time frame include:
- Alcohol Consumption History – Heavy, long-term alcohol use leads to more intense withdrawal symptoms. The longer and more frequently someone drinks, the more likely they are to experience prolonged and severe withdrawal.
- Overall Health – Those with good physical health may experience a smoother withdrawal process. Preexisting conditions, such as liver disease or nutritional deficiencies, can make withdrawal symptoms worse and prolong recovery time.
- Mental Health Conditions – Anxiety, depression, or other mental health disorders can worsen withdrawal symptoms. People with co-occurring mental health conditions may need additional treatment to manage both their psychological and physical symptoms effectively.
- Medical Supervision – Withdrawal in a medically supervised setting is often shorter and safer compared to attempting detox at home. Medical detox ensures that withdrawal symptoms are managed appropriately with medication, hydration, and nutritional support, reducing the risk of severe complications like seizures or delirium tremens (DTs).

Treatment Options for Alcohol Withdrawal
The alcohol detox process can last anywhere from a few days to a week, depending on individual circumstances.
Medical Detox: The Safest Option
Attempting alcohol detox at home is dangerous, especially for individuals with severe dependence. Medical detox at a recovery center provides professional supervision, ensuring that withdrawal symptoms are managed safely. Medical professionals can provide medications to prevent complications such as seizures and delirium tremens (DTs), making the process safer and more comfortable.
Medications for Withdrawal Symptoms
Doctors may prescribe medications to ease withdrawal symptoms. Benzodiazepines, such as diazepam and lorazepam, help reduce anxiety, prevent seizures, and manage symptoms. Anticonvulsants may also be used in some cases to prevent seizures. Additionally, beta-blockers can help control heart rate and blood pressure, reducing the physical strain of withdrawal.
Importance of Hydration, Nutrition, and Rest
Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids is essential to prevent dehydration, which is common during alcohol withdrawal. Maintaining a nutritious diet helps support physical recovery by replenishing lost nutrients and strengthening the body. Additionally, getting adequate rest allows the body to heal and regain energy, making the withdrawal process more manageable.
Therapies and Counseling Options
Support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) provide peer support, allowing individuals to connect with others who understand their struggles and share coping strategies. Online counseling can be an accessible resource for many people, offering flexible therapy options that fit into different schedules and lifestyles.
FAQs About Alcohol Withdrawal
When does alcohol withdrawal start?
Alcohol withdrawal symptoms typically begin 6–12 hours after the last drink, depending on individual factors such as drinking history and overall health.
How long do alcohol withdrawal symptoms last?
Most withdrawal symptoms last between 3–7 days, but some individuals may experience lingering symptoms, such as anxiety and insomnia, for weeks or months.
How long after you quit drinking does your body return to normal?
The body begins to heal immediately after quitting alcohol, but full recovery can take weeks to months, depending on individual health and alcohol consumption history.
Can alcohol withdrawal be life-threatening?
Yes, alcohol withdrawal can be life-threatening due to severe symptoms like delirium tremens (DTs) and seizures. Medical supervision is recommended for individuals at risk.
Find Safe and Effective Alcohol Withdrawal Treatment With Lumina Recovery
The alcohol withdrawal timeline is a highly individual experience, with its challenges varying greatly from person to person. While the process can be daunting, understanding the timeline, symptoms, and available treatments can provide a roadmap for those embarking on this journey.
It’s important to remember that detox is just the first step toward recovery. Lumina Recovery’s alcohol addiction programs help build long-term success through ongoing treatment, lifestyle changes, and support from healthcare professionals, family, and peer groups.
If you or someone you love is struggling, contact Lumina Recovery today.
Source:

6 Celebrities With Alcohol Addiction Recovery Stories That Inspire
While celebrities often grace our screens and lives with their talent and charisma, they are not immune to life’s challenges, including the grip of addiction.
Below, we’ll highlight the inspiring journeys of well-known figures who, despite their fame and admiration, have struggled with alcohol addiction.
More importantly, we’ll celebrate their commitment to sobriety, showcasing how each of these celebrities has successfully embraced a sober lifestyle. Their stories are not just tales of stardom and struggle—they are powerful testaments to resilience, hope, and the strength of the human spirit in overcoming addiction.
1. Stephen King
Stephen King’s journey to sobriety began in the 1980s, catalyzed by a family intervention.
In an interview with The Guardian, King reflected on his addiction to alcohol, noting a poignant moment when he was caught drinking at his son’s little league game.
He compares his experiences to those of his character Danny in Doctor Sleep, acknowledging that his own rock bottom was less dramatic but equally transformative.1
King’s story is not just about overcoming addiction—it’s a powerful narrative of personal growth and the profound impact that reaching one’s lowest point can have in moving toward a meaningful change in life.
2. Ben Affleck
Ben Affleck, in a 2020 interview on ABC’s Nightline, shared his struggles with alcoholism. He discussed his attempts to “drink like a normal person,” only to find his situation escalating. Affleck also spoke about his family history with alcoholism and his desire to prevent his children from witnessing him struggle with the same issues.2
His story highlights the complex nature of addiction and the power of personal resolve in overcoming such challenges.
Affleck’s openness in sharing his experiences serves as an encouragement to others facing similar battles, showing that despite the difficulties, change and recovery are achievable goals.
3. Drew Barrymore
Drew Barrymore’s journey from child stardom to sobriety is a compelling tale of resilience and self-reinvention.
As detailed in a 2023 LA Times article, Barrymore’s ascent to fame at a young age came with unique challenges. Treated like an adult in the world of Hollywood, she was exposed to drugs and alcohol early in her life, setting the stage for struggles with substance abuse.
Following a period of turmoil and a relapse after her divorce, Barrymore made a decisive choice to give up alcohol for good.3
Her ability to remain positive and successful despite a rocky and traumatic childhood is not only commendable but also serves as an inspiration to those who have endured similar traumatic experiences.
Barrymore’s story underscores the possibility of overcoming a troubled past and emerging stronger, providing hope and encouragement to others facing their own battles with addiction and adversity.
4. Tim McGraw

Country music star Tim McGraw opened up about his past struggles with alcohol in an essay in Esquire.
He recalls a harrowing moment, taking a shot early in the morning, which led him to seek help from his wife, Faith Hill. Her support, he admits, was life-changing. McGraw credits his family for motivating him to become sober and replaces his addiction with a rigorous fitness regimen.4
This journey is not only a testament to his personal strength and resilience but also serves as a hopeful message to others struggling with similar challenges, illustrating the power of support, determination, and the possibility of positive change.
5. Demi Lovato
Demi Lovato’s journey through addiction, as revealed in a Variety interview, began at a very young age in the form of alcohol abuse and intensified following a car accident at 13, leading to opioid use.5
Their early rise to fame as a child star, coupled with struggles of an eating disorder and the challenging journey of self-identity, fueled their descent into substance abuse.
Lovato’s openness about these struggles offers a deeply personal view into the complexities of fame, mental health, and identity, highlighting their resilience and ongoing commitment to a sober lifestyle, despite the multifaceted challenges they faced. Their story is not only a reflection of their personal struggles but also a beacon of hope for others battling similar issues.
6. Daniel Radcliffe
Daniel Radcliffe’s candid discussion about how he struggled with alcohol addiction, as shared in an interview on the Off Camera Show, highlights the often unspoken pressures of fame. In his interview, Radcliffe speaks openly about how the constant attention he experienced from an early age and expectation to always appear pleasant contributed to his drinking.
This pressure, coupled with the challenges of managing a public persona, led him down a path of alcohol dependency.
However, Radcliffe’s story doesn’t end there. He credits his success in achieving sobriety to a robust support system and a crucial moment of self-realization. One morning, he woke up and acknowledged that he was in a bad situation, a pivotal step that led him towards recovery.6
Radcliffe’s journey underscores the importance of acknowledging one’s circumstances and the crucial role of support networks in overcoming addiction. His story is a powerful testament to the possibility of change, offering hope and encouragement to others who may be facing similar challenges in their lives.
Your Path to Recovery Awaits
Alcohol addiction is a challenge that spans all walks of life, and these stories of celebrities are poignant reminders that you are not alone in this struggle. Their journeys of overcoming addiction and embracing sobriety offer hope and inspiration, demonstrating that change is possible with the right support.
At Lumina Recovery, we understand the complexities of addiction, and our comprehensive alcohol addiction rehabilitation programs are designed to provide the support and care needed for a successful recovery.
Remember, taking the first step towards recovery can lead to a transformative journey, much like the stories shared here.
If you or someone you know is struggling with drug or alcohol addiction, we are here to help guide you on the path to a healthier, sober life. Reach out to Lumina Recovery today.
Sources:
- https://www.theguardian.com/books/2013/sep/21/stephen-king-shining-sequel-interview
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QDEUhJiCCV4
- https://www.latimes.com/entertainment-arts/story/2023-03-05/for-real-drew-barrymore-talk-show
- https://www.esquire.com/entertainment/music/a37227738/tim-mcgraw-what-ive-learned-interview-2021/
- https://variety.com/2022/music/news/demi-lovato-disney-channel-addiction-eating-disorder-1235352623/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FfCsVPJsw-E

How Long Does Alcohol Stay in Your System?
The length of time alcohol stays in your system depends on several factors, including your metabolism, age, weight, gender, and how much you drink. On average, the body metabolizes alcohol at a rate of about one standard drink per hour.1 However, alcohol can still be detected in different ways for varying amounts of time.
A blood test may detect alcohol for 1 to 2 days, a breath test for 4 to 6 hours, and standard urine tests for 12 to 24 hours. In hair, alcohol can be detected for up to 90 days.1,2
These timelines can vary based on how your body processes alcohol, so the exact amount of time it stays in your system differs from person to person.
Factors Influencing Alcohol Metabolism
Alcohol metabolism varies from person to person due to biological and lifestyle factors. These elements play a role in how quickly the body processes alcohol and eliminates it.
Biological Factors
- Age: As people age, their metabolism slows, leading to longer alcohol retention.
- Gender: Women generally metabolize alcohol more slowly than men due to differences in body composition and enzyme levels.
- Body Composition: Individuals with higher body fat tend to retain alcohol longer since fat does not absorb alcohol.
- Genetics: Genetic variations influence enzyme activity responsible for processing alcohol.
Lifestyle Factors
- Diet and Eating Patterns: Consuming food before or during alcohol consumption slows its absorption into the bloodstream, especially in the small intestines.
- Physical Activity Levels: Regular exercise may contribute to a faster metabolism but does not significantly impact alcohol elimination.
- Overall Health Status: Liver function, hydration levels, and underlying medical conditions affect how long alcohol stays in your system.

Alcohol Detection Timelines
Different testing methods detect alcohol for varying durations. Here are the common detection windows:
- Blood Test: Alcohol remains detectable in the blood for 1 to 2 days.2
- Breath Test: Breathalyzers can detect alcohol for approximately 4 to 6 hours.1
- Urine Tests: Standard urine tests detect alcohol for 12 to 24 hours.1
- Sweat Testing: The detection window for alcohol in sweat is hours to weeks.2
- Hair Tests: Alcohol can be detected in hair follicles for up to 90 days.1
What Is Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC)?
Blood alcohol concentration (BAC) is a measurement of the amount of alcohol present in the bloodstream. Having a BAC of 0.02% and above is considered unsafe and driving with a BAC of 0.08% or higher is illegal in the United States.1 High BAC levels may cause blacking out, which can be life-threatening.
BAC levels are influenced by several factors, including the quantity and rate of alcohol consumption, body weight and composition, and individual metabolic rates. Lighter individuals generally experience higher BAC levels with the same alcohol intake compared to heavier individuals.
A standard drink contains 14 grams (0.6 ounces) of pure alcohol, and consuming multiple drinks in a short time can cause BAC to rise rapidly.1 People with faster metabolisms process alcohol more quickly, leading to a faster decline in BAC.
Common Myths About Alcohol Metabolism
There are many misconceptions about how to speed up alcohol metabolism. Here are a couple myths about alcohol metabolism debunked:
- Myth: Drinking coffee accelerates sobriety.
Reality: Coffee may increase alertness but does not affect alcohol metabolism. The liver still metabolizes alcohol at the same rate, regardless of caffeine intake. While coffee can help a person feel more awake, it does not reduce BAC levels or eliminate alcohol from the body any faster.
- Myth: Physical activity can help “sweat out” alcohol.
Reality: Exercise does not significantly speed up alcohol elimination. While small amounts of alcohol may leave the body through sweat, the vast majority is processed by the liver. Engaging in physical activity may improve alertness and help with hangover symptoms, but it does not accelerate the breakdown of alcohol in the bloodstream.
Health Implications of Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol affects both short-term and long-term health.
Short-Term Effects
- Impaired judgment and coordination
- Increased risk of accidents and injuries
- Risk of alcohol poisoning, which can be life-threatening
Long-Term Effects
- Liver Disease: Chronic alcohol use can lead to cirrhosis and liver failure.
- Cardiovascular Issues: High alcohol intake increases the risk of high blood pressure and heart disease.
- Dependence and Addiction: Prolonged alcohol use may lead to addiction, requiring professional intervention.

When and How to Seek Help
If you or a loved one is experiencing any of these signs, it may be time to seek professional support. Early intervention can make a significant difference in recovery outcomes. Here’s how to take the next step:
- Consult a healthcare provider. A doctor or addiction specialist can assess the severity of alcohol use and recommend appropriate treatment options.
- Explore treatment programs. Options range from detox programs to outpatient and inpatient rehabilitation, depending on individual needs.
- Join a support group. Group therapy and support meetings provide peer support and guidance for individuals working toward sobriety.
- Consider therapy. Behavioral therapies like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals address underlying triggers and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
FAQs
How long does alcohol stay in your blood?
Alcohol can be detected in your blood for 1 to 2 days.
Can drinking water or eating food speed up the elimination of alcohol from your system?
While hydration and food can slow alcohol absorption, they do not speed up its metabolism.
How does body weight and gender affect alcohol metabolism?
Women and individuals with lower body weight typically process alcohol more slowly, leading to higher BAC levels.
What are the risks of driving the day after heavy drinking?
Residual alcohol in your system can impair reaction time and judgment, increasing accident risk. It depends on the amount of time that has passed since drinking.
How accurate are home breathalyzer tests in measuring blood alcohol concentration?
Home breath tests provide an estimate but may not always be as accurate as professional-grade devices.
Take Control of Your Recovery Journey With Lumina Recovery
Understanding how long alcohol stays in your system and how tests can detect alcohol can help individuals make safer, more responsible decisions about drinking. It’s important to recognize when alcohol use is interfering with daily life, relationships, or health.
If you or someone you love is struggling with alcohol dependence, Lumina Recovery provides holistic alcohol treatment programs, including dual diagnosis treatment. Our evidence-based therapies and expert support help individuals break free from alcohol addiction and build a healthier, sober future.
Contact us today to start your journey to a healthier, alcohol-free life.
Sources:
- Heathline. How Long Does Alcohol Stay in Your Body?.
- McNeil SE, Chen RJ, Cogburn M. Drug Testing. [Updated 2023 Jul 29].

Is Alcohol a Drug?
When we think of drugs, images of illicit substances or prescription medications might come to mind. However, there’s one commonly used substance that often escapes this category in everyday conversations: alcohol. Our goal is to provide insights that can help you understand alcohol’s nature, its effects on the body, and its role in our lives.
What defines a ‘drug’?
Excluding food and water, a drug is any substance that, when taken into the body, alters its function either physically or psychologically. This broad definition encompasses a wide range of substances.
Drugs can be legal, like prescription medications and over-the-counter remedies, or illegal, like many controlled substances. They can also be natural, like some herbal remedies, or synthetic, created in laboratories.
The key aspect is their ability to affect a person and change how the body or mind works, whether it’s to relieve pain, alter mood, enhance performance, or provide some other effect.
How does alcohol fit into the definition of a drug?
Alcohol is a perfect example of a drug under this definition. It’s a chemical substance known as ethanol, produced by the fermentation of sugars by yeasts.
When consumed, it’s absorbed into the bloodstream and affects the central nervous system (CNS), particularly the brain.
Alcohol’s impact ranges from mild mood alterations to significant behavioral changes. It acts as a depressant, slowing down vital functions resulting in slurred speech, unsteady movement, disturbed perceptions, and an inability to react quickly.
Its effects are highly dependent on the amount consumed and individual differences in body chemistry and tolerance.
Why is alcohol often not perceived as a drug?
The perception of alcohol as something other than a drug is primarily cultural and historical.
For centuries, alcohol has been a part of social rituals, religious ceremonies, and daily life in many societies. This long history has led to its normalization, often viewing it as distinct from ‘drugs,’ which are typically associated with illegal, harmful substances.
Furthermore, the legal status of alcohol in most countries reinforces this perception. Unlike many controlled substances, alcohol is legally produced, sold, and consumed, further distancing it from the typical drug stereotype.
However, this distinction can be misleading, as alcohol shares many characteristics with other substances classified as drugs, including the potential for abuse and dependency, leading to health problems.
What are the effects of alcohol on the body and mind?
Alcohol’s effects are wide-ranging and can vary greatly from person to person.
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) says that young people in the United States are at risk of alcohol misuse and binge drinking during their high school years—a time when the brain is still actively developing and can be altered by alcohol.1
In the short term, even a small amount of alcohol affects the brain, leading to lowered inhibitions and a feeling of relaxation. As consumption of alcohol increases, the impact becomes more pronounced. This can include impaired judgment, slowed reflexes, distorted vision, memory lapses, and even blackouts.
Over the long term, chronic alcohol use can lead to serious health issues, including liver disease, heart problems, and an increased risk of certain cancers. It can also exacerbate mental health issues such as depression and anxiety and can lead to lasting changes in brain function.
Is alcohol addictive?
Yes, alcohol can be highly addictive. The risk of developing an addiction from drinking alcohol, known as alcohol use disorder (AUD), is influenced by various factors including genetics, personal history, emotional health, and social environment.
The addictive nature of alcohol is due to its effects on the brain’s reward system. Regular consumption can lead to tolerance, where more alcohol is needed to achieve the same effect, and dependence, where the body starts to rely on alcohol to function normally.
Withdrawal symptoms can occur if a dependent person stops drinking, which can range from mild anxiety and shakiness to severe complications such as seizures and delirium tremens (DTs).
Can alcohol be used safely?
While alcohol can be consumed safely by many adults, it’s essential to understand and respect its potential risks.
Safe consumption means different things for different people, depending on factors like age, gender, medical history, and family history of alcoholism.
For some, abstaining from alcohol is the safest option. For others, moderate drinking may not present significant health risks, but always talk to your doctor about what is right for you.
How can you recognize an alcohol problem?
Recognizing an alcohol problem can be challenging, especially since alcohol use is socially accepted in many cultures. Key indicators include:
- Increased tolerance, which is needing more alcohol to achieve the same effect
- Withdrawal symptoms, such as shakiness, sweating, nausea, or anxiety after a period without alcohol
- Losing control over drinking habits
- Neglecting responsibilities at work, school, or home due to drinking
- Continuing to drink despite social or interpersonal problems worsened by alcohol
- Spending a great deal of time obtaining, using, or recovering from the effects of alcohol
Often, individuals may downplay or deny these signs, making self-recognition of these problems difficult. It’s important to approach these concerns with compassion, both for oneself and for others who may be struggling.

Where can someone get help for alcohol addiction?
There are numerous avenues for seeking help with alcohol addiction, emphasizing that no single approach is suitable for everyone.
Treatment options include professional counseling, which can provide strategies for coping with cravings and avoiding triggers. Support groups offer communal understanding and shared experiences.
For some, inpatient or outpatient rehabilitation programs provide structured treatment environments. Addressing underlying mental health issues, such as anxiety or depression, with a healthcare provider is crucial.
Lumina Recovery’s Commitment to Understanding and Healing
Understanding alcohol as a drug can be a crucial step in recognizing its potential impacts and risks. As with any substance that alters how our body and mind function, it’s important to be informed and cautious. If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol use, remember that help is available, and taking the first step towards recovery is a sign of strength and hope.
Remember, at Lumina Recovery, we’re here to offer support and guidance on your journey to understanding and managing alcohol use. You’re not alone in this, and we’re committed to providing a safe, understanding, and knowledgeable environment to help you navigate these challenges.
If you or someone you love is struggling, contact Lumina Recovery today.
Sources:

8 Facts About Alcohol Cravings and How to Beat Them
Alcohol cravings are a common challenge for individuals in recovery, often posing obstacles to long-term sobriety. Understanding what causes them and how to stop alcohol cravings effectively is crucial for sustaining a healthier lifestyle.
By learning about the psychological, physiological, and environmental factors that trigger cravings, individuals can develop strategies to curb alcohol cravings and stay on track with their recovery journey.
What Are Alcohol Cravings?
Alcohol cravings refer to the intense desire or urge to consume alcohol, often triggered by both psychological and physiological factors. These cravings can be influenced by changes in brain chemistry due to prolonged alcohol use, making them difficult to control without proper strategies in place.
While cravings do not necessarily indicate a relapse, learning how to reduce alcohol cravings is essential for maintaining sobriety.
Causes of Alcohol Cravings
Several factors contribute to alcohol cravings, including:
- Neurological Changes: Long-term alcohol consumption alters brain chemistry, particularly affecting dopamine and serotonin levels, which influence reward and pleasure.
- Environmental Triggers: Certain settings, such as bars, parties, or locations associated with past drinking habits, can trigger cravings.
- Emotional States: Stress, anxiety, depression, and other emotional states can lead individuals to seek alcohol as a coping mechanism.
Common triggers for alcohol cravings include:
- Social Situations: Being around people who drink or in environments where alcohol is present.
- Stress and Anxiety: Work pressure, personal conflicts, or financial struggles can lead to cravings.
- Routine and Habitual Patterns: Certain times of the day or specific activities associated with past drinking behavior.
- Sensory Cues: Smelling alcohol, seeing someone else drink, or even watching alcohol-related advertisements.

8 Facts About Alcohol Cravings
Alcohol cravings are a natural part of the recovery process, but they don’t have to control your journey. Understanding the facts about alcohol cravings can help you develop effective strategies to manage them and maintain long-term sobriety.
1. Cravings Are Temporary
If you are wondering when alcohol cravings stop, it varies from person to person, but they tend to diminish over time with proper coping strategies.
Although they can feel intense, they will pass with time and proper management techniques. Recognizing their temporary nature can help individuals avoid acting on them impulsively.
2. Hydration Helps
Drinking water or other non-alcoholic beverages can reduce the intensity of cravings. Dehydration can sometimes be mistaken for hunger or an alcohol craving, so staying properly hydrated can be beneficial in minimizing urges.
3. Exercise Can Reduce Cravings
Engaging in physical activity releases endorphins, which naturally elevate mood and reduce stress. Exercise has been shown to lower the intensity and frequency of alcohol cravings while promoting overall well-being.
4. Cravings Can Decrease Over Time
The longer a person maintains sobriety, the weaker their cravings tend to become. As the brain heals and new coping mechanisms are developed, the urge to drink often diminishes. While the timeline varies by individual, cravings tend to subside significantly after the first few months of sobriety.
5. Cravings Do Not Equal Relapse
Experiencing cravings is a normal part of recovery and does not mean that someone is failing. Recognizing that cravings do not have to lead to relapse empowers individuals to implement effective coping strategies and maintain their sobriety.
6. Stress Increases Cravings
Chronic stress is a significant trigger for alcohol cravings. Developing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, therapy, and relaxation exercises, can help mitigate cravings caused by stress and anxiety.
7. Healthy Eating Can Help Manage Cravings
If you are experiencing a strong craving for alcohol, eating a nutritious meal may help lessen the intensity of the urge. A well-balanced diet rich in protein, fiber, and complex carbohydrates can stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce cravings. Nutrient deficiencies, particularly in B vitamins and magnesium, can exacerbate the desire for alcohol.
8. Sleep Impacts Cravings
Lack of sleep can lead to stronger alcohol cravings and poor decision-making. Maintaining a healthy sleep schedule helps regulate mood and reduces the likelihood of turning to alcohol for relief.

Strategies to Manage and Overcome Alcohol Cravings
When cravings arise, individuals can use the following techniques:
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Practicing slow, deep breathing can help reduce stress and refocus the mind.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Grounding techniques, such as focusing on the present moment, can diminish the power of cravings.
- Distraction Methods: Engaging in hobbies, taking a walk, or calling a friend can help shift focus away from the craving.
To maintain sobriety in the long run, individuals can implement these strategies:
- Evidence-Based Therapies: Therapies like CBT, DBT, and EMDR help individuals recognize and change thought patterns that lead to cravings.
- Building a Support Network: Connecting with support groups, attending therapy, and surrounding oneself with positive influences can reinforce sobriety.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting healthier habits, such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and structured routines, can reduce exposure to triggers.
FAQs
How do you stop alcohol cravings?
Combining short-term coping mechanisms, long-term strategies like therapy and lifestyle changes, and medical interventions can effectively help with alcohol cravings.
What helps with alcohol cravings?
Mindfulness, therapy, medications, exercise, and a strong support system are all effective ways to curb alcohol cravings.
How to curb alcohol cravings?
Identifying triggers, developing coping techniques, and making lifestyle changes can significantly reduce alcohol cravings over time.
When do alcohol cravings go away?
While cravings may decrease in intensity and frequency over time, they can still be triggered by stress or environmental cues. Managing them is key to long-term recovery.
Take Control of Alcohol Cravings With Lumina Recovery
Managing alcohol cravings is an essential step toward long-term sobriety. Understanding their root causes, identifying triggers, and implementing effective coping strategies can empower individuals to overcome urges and build a healthier future. With the right support, cravings do not have to lead to relapse.
At Lumina Recovery, we offer cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to help individuals reframe their thought patterns and medication-assisted treatment (MAT) to ease cravings and support recovery. Our evidence-based programs provide the tools necessary to navigate cravings and achieve lasting sobriety.
If you or a loved one is struggling with alcohol cravings, reach out to Lumina Recovery today and take the first step toward a healthier, alcohol-free life.
The Dangers of Mixing Ambien and Alcohol
In recent years, there’s been a significant increase in the prescription of sleep aids, with Ambien being one of the most commonly prescribed.
While Ambien is effective in treating sleep disorders, its interaction with alcohol is a growing concern. Mixing Ambien and alcohol, a practice some individuals engage in, either knowingly or unknowingly, can lead to severe consequences, both physically and mentally.
Below, we aim to shed light on this dangerous combination, discussing the risks, the science behind these interactions, and what to do if you are struggling with Ambien and alcohol.
What Is Ambien?
Ambien, known generically as zolpidem, is a sedative-hypnotic medication primarily prescribed for treating insomnia.
Its main function is to aid in falling asleep and staying asleep, especially in cases where sleep disturbances significantly impact daily life.
Ambien works by slowing down brain activity, allowing for a state of sleep.
Its effectiveness in the short-term management of sleep disorders has made it a popular prescription choice among healthcare professionals.
However, it’s crucial to understand that Ambien is meant for short-term use, primarily because of its potential for dependence and tolerance.
The Risks of Mixing Ambien and Alcohol
Mixing Ambien with alcohol is not only medically discouraged but can also lead to a range of serious and potentially life-threatening side effects, which we will explore in detail below:1,2,3
- Enhanced Sedation and Drowsiness: Both Ambien and alcohol are central nervous system depressants. When combined, they significantly increase sedation, leading to extreme drowsiness, which can be dangerous, especially if operating machinery or driving.
- Impaired Cognitive and Motor Functions: This combination can impair judgment, coordination, and reaction times. These effects combined can increase the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Increased Risk of Overdose: Mixing alcohol with Ambien raises the risk of overdose, as both substances can enhance each other’s effects. Symptoms of overdose may include severe drowsiness, confusion, shallow breathing, fainting, or even coma.
- Respiratory Issues: Both alcohol and Ambien can slow down breathing. When taken together, this effect is magnified, potentially leading to respiratory failure.
- Memory Problems: Users may experience memory lapses or blackouts, leading to a loss of consciousness without remembering what happened.
- Worsening of Mental Health Conditions: Those with a history of depression or other mental health conditions may experience a worsening of their symptoms.
- Dependency and Withdrawal Issues: Using Ambien with alcohol can increase the risk of dependence on both substances and may lead to complex withdrawal symptoms if use is stopped.
- Sleep-Walking and Other Complex Behaviors: There are reports of people engaging in activities like sleep-walking, sleep-driving, and other unusual behaviors while under the influence of Ambien and alcohol, without any memory of these actions.
- Increased Risk of Sleep-Related Eating Disorders: Combining these substances can lead to unusual nocturnal eating patterns, which can be dangerous and lead to other health issues.
- Amplified Side Effects: Each substance’s side effects, such as dizziness, nausea, and vomiting, can be amplified when taken together, leading to greater discomfort and health risks.
Understanding the Dangers
The risks associated with mixing Ambien and alcohol extend beyond immediate physical effects, delving into the realm of complex physiological and neurological impacts.
Ambien is designed to induce sleep, but adding alcohol to the mix disrupts this process and leads to worse sleep quality, contrary to Ambien’s purpose. This combination not only fails to effectively treat insomnia but may worsen it.
Moreover, mixing Ambien and alcohol can intensify mental health problems. Individuals with conditions like depression or anxiety might see their symptoms get worse.
The combined effect on the brain can cause severe cognitive issues, such as reduced alertness and poor judgment, heightening the risk of accidents or risky behavior.
In the long run, the full impact of regularly mixing Ambien and alcohol isn’t entirely known, but the available evidence suggests it could cause lasting harm to brain function and mental health.
Addiction to Ambien and Alcohol

Combining alcohol with Ambien may heighten the risk of addiction, primarily due to their addictive effects compound.
Both substances, when used independently, carry a potential for dependence; however, when combined, this risk is amplified.
Ambien, a medication prescribed for insomnia, can lead to habit formation, especially with prolonged or higher-than-recommended use.
Alcohol, being a central nervous system depressant, enhances the sedative effects of Ambien.
This dual action can not only increase the immediate health risks but can also accelerate the pathway to dependency on both substances.
The compounded nature of this risk is particularly concerning, as it creates a more complex scenario for addiction treatment and recovery.
Individuals using both substances are therefore at a higher risk of developing a more severe addiction compared to using either substance alone.
The Path to Sobriety Begins at Lumina Recovery
The dangers of mixing Ambien with alcohol are clear, with risks ranging from severe health complications to heightened addiction potential.
At Lumina Recovery, we offer specialized treatment programs for drug and alcohol addiction, including those involving co-occurring addictions.
We’re dedicated to guiding individuals through their recovery journey and offering the support and tools necessary for achieving long-term sobriety.
If you or someone you know is struggling with addiction, Lumina Recovery is here to help on the path to recovery and wellness. Contact us today.
Sources:

The Effects of Long-Term Alcohol Use
In a world where alcohol plays a prominent role in many cultures and social settings, understanding its long-term effects on our bodies and minds is crucial. While social drinking can be part of a balanced lifestyle with short-term effects, the line between moderate and excessive use can often blur, leading to significant health risks.
We want to explore the often under-discussed long-term consequences of alcohol consumption, focusing not just on physical health, but also on mental well-being, relationships, and daily life.
Effects on Physical Health
Long-term alcohol use increases the risk of developing alcohol use disorder and can have a myriad of effects on the body, with the severity depending on factors like the amount and frequency of consumption. Key areas impacted include:1,2,3
Liver
The liver is particularly vulnerable. Alcohol abuse can lead to fatty liver, an early stage of liver disease that can progress to alcoholic hepatitis (inflammation and destruction of liver tissue).
It eventually can lead to cirrhosis, where normal liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue, significantly impaired liver function. Both moderate drinking and binge drinking have effects on the liver’s long-term health.
Heart and Circulatory System
Chronic alcohol use can cause cardiomyopathy (weakening of the heart muscle), arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat), high blood pressure, and an increased risk of stroke. These conditions can have long-term impacts on overall cardiovascular health.
Digestive System
Alcohol interferes with the digestive process, leading to problems absorbing nutrients and vitamins. It can cause damage to the tissues in the digestive tract, leading to conditions like gastritis and ulcers.
Cancer Risk
Long-term alcohol use is linked to an increased risk of several types of cancers, including mouth, throat, liver, breast, and colorectal cancers.
In particular, the risk of breast cancer is higher in women even when consuming small amounts of alcohol. The risk is compounded by factors like smoking, poor nutrition, and a weakened immune system.
Effects on Mental Health
The mental health effects of prolonged alcohol use are diverse and significant, including:3,4
Mood Disorders
Alcohol can act as a depressant, exacerbating symptoms of depression and anxiety. Over time, this can lead to a chronic state of mental health decline.
Cognitive Impairments
Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to deficits in cognitive functions, including problems with memory, learning, and decision-making. In severe cases, it can result in permanent brain damage and conditions like Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, a severe memory disorder.
Alcohol Dependency and Addiction
Prolonged use can lead to a physical and psychological dependence on alcohol, characterized by a strong craving for alcohol, loss of control over its use, and withdrawal symptoms when not drinking.
Effects on Relationships and Daily Life
The impact of long-term alcohol use on relationships and daily life can be widespread and deeply damaging.
Relationship Strain
Alcohol dependency can often lead to interpersonal problems, including conflicts with family members, friends, and colleagues. It can result in neglect of social, occupational, or recreational activities, further straining relationships.
Occupational Impact
Work performance may suffer due to absenteeism, lack of focus, or alcohol-related health problems. This can lead to job loss and financial difficulties.
Legal Issues
There may be legal consequences, such as DUIs or other alcohol-related offenses, which can further complicate personal and professional life.
Mental Health
Chronic alcohol use can lead to isolation, exacerbation of mental health issues, and an overall decline in quality of life.
Alcohol Dependency
Alcohol dependency, commonly referred to as alcoholism, is a serious condition that often arises from long-term alcohol use.
Craving: A strong and ongoing compulsion to drink alcohol.
Loss of Control: The inability to limit drinking on any given occasion.
Physical Dependence: Experiencing withdrawal symptoms when not drinking, such as nausea, sweating, shakiness, and anxiety.
Tolerance: The need to drink greater amounts of alcohol to get the same effect.
The development of alcohol dependency involves changes in the brain’s neurochemistry. Long-term alcohol use can alter the balance of neurotransmitters, affecting systems related to reward, motivation, and stress.5
This makes quitting difficult and often requires professional treatment, including detoxification, counseling, medication, and support groups.
Reversing the Effects

The potential for reversing the effects of long-term alcohol use is largely dependent on a range of factors, including the duration and severity of the alcohol use.
Physical Health
Abstaining from alcohol can lead to remarkable improvements in physical health, including the healing of liver conditions, stabilization of heart and circulatory functions, and restoration of digestive health.
These changes, accompanied by a healthy lifestyle, can significantly reverse the physical damages caused by long-term alcohol use.6
Mental Health
Mental health can greatly benefit from sobriety, with treatments for mood disorders and cognitive impairments often showing positive results.
Simultaneously, addressing alcohol dependency through professional rehabilitation and treatment, including therapy and support groups, can break the cycle of addiction, leading to a more stable and fulfilling life.
Relationships and Social Life
Recovery fosters improved relationships and social interactions.
As individuals regain control over their lives, they often find renewed strength in mending strained relationships and enhancing their work and social life, contributing to overall well-being and happiness.
How to Stop the Effects of Long-Term Use
Ceasing the effects of long-term alcohol use and addiction involves a comprehensive approach.
Acknowledgement and Acceptance: Recognizing the problem and having the willingness to address it is the first crucial step.
Professional Help: Treatment options include medically assisted detoxification, behavioral therapies, counseling, and support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous. Medications may be prescribed to manage withdrawal symptoms and prevent relapse.
Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle is critical. This includes a nutritious diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques.
Support Systems: Strong support from family, friends, and support groups can provide the emotional and practical support needed for recovery.
Ongoing Management: Recovery from alcohol dependency is an ongoing process. It often involves continuous participation in support groups and sometimes long-term counseling.
Lumina Recovery Is Here to Help
The journey of understanding and coping with the effects of long-term and excessive alcohol use is complex and deeply personal. It’s a path marked by challenges, but also by opportunities for growth and healing.
Recognizing the impact of alcohol on various aspects of life is the first step towards positive change. It’s important to remember that struggling with alcohol does not define you and seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
With the right support and resources, recovery and a healthier, more fulfilling life are within reach. We encourage individuals facing these challenges to take that brave first step towards change and healing.
If you or someone you love is struggling with alcoholism, reach out to Lumina Recovery today.
Sources:
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/alcohol-related-liver-disease-arld/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513322/
- https://www.cdc.gov/alcohol/index.html
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6875727/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2923844/
- https://arcr.niaaa.nih.gov/volume/41/1/natural-recovery-liver-and-other-organs-after-chronic-alcohol-use#article-toc2

Signs of Drug or Alcohol Addiction
Identifying the warning signs of addiction in a loved one can be challenging, but early recognition is crucial for getting them the help they need. The symptoms of addiction can vary widely, from noticeable changes in physical appearance and health to shifts in behavior, mood, and relationships. For family and friends, understanding these signs of an addiction can make all the difference in supporting a loved one struggling with substance use.

10 Warning Signs Your Loved One May Be Struggling With Addiction
Recognizing the warning signs of addiction early can help a loved one get the support they need. What signs show substance use disorder?
While every individual’s experience with addiction is unique, here are 10 common signs of drug abuse that may indicate a substance abuse problem. These signs of addiction may include changes in appearance, mood swings, financial struggles, and risky behaviors.
1. Noticeable Changes in Appearance and Hygiene
One of the early signs of addiction is a decline in personal hygiene and grooming habits. If your loved one suddenly stops caring about their appearance, frequently wears dirty clothes, or looks disheveled, this could be one of the substance abuse signs to watch for.
2. Unexplained Weight Loss or Weight Gain
Substance use can impact appetite and metabolism, leading to drastic changes in weight. Signs of addiction may include sudden weight loss caused by stimulants or significant weight gain due to alcohol or depressants.
3. Bloodshot Eyes, Dilated or Constricted Pupils
Drugs and alcohol can cause visible changes in the eyes. Common signs of drug abuse include red, bloodshot eyes or pupils that appear unusually small or large, even in normal lighting.
4. Sudden Mood Swings, Irritability, or Emotional Instability
Drastic mood swings are common behaviors of substance abuse. Individuals struggling with addiction may experience bouts of anger, depression, or extreme irritability without an obvious cause. If your loved one’s personality has noticeably changed, this could be a drug addiction warning sign.
5. Increased Secrecy and Deceptive Behavior
A person with a substance abuse problem may become secretive about their whereabouts, frequently lie, or avoid answering questions about their activities. They may also become defensive when confronted about their behavior.
6. Changes in Sleep Patterns and Energy Levels
An addiction sign may include disrupted sleep. Your loved one might sleep excessively, suffer from insomnia, or seem constantly exhausted. These warning signs of substance abuse can severely impact daily responsibilities.
7. Withdrawing From Family and Friends
One of the most noticeable signs of substance use is a shift in social behavior. Individuals struggling with addiction may isolate themselves, avoid family gatherings, or stop engaging in hobbies they once enjoyed.
8. Risk-Taking and Reckless Behavior
A person exhibiting behaviors of substance abuse may engage in risky activities, such as driving under the influence, unsafe sexual behavior, or using drugs in dangerous environments. Increased risk-taking is a significant sign of addiction and should not be ignored.
9. Financial Problems and Unexplained Expenses
If your loved one frequently borrows money, sells personal items, or struggles to pay bills without a clear reason, it may indicate signs of an addiction. Many individuals with addiction issues go to great lengths to fund their substance use.
10. Declining Performance at Work or School
One of the warning signs of addiction is a drop in work or academic performance. Missing deadlines, frequent absences, and a loss of motivation may indicate a deeper substance abuse problem.

What to Do If You Notice These Signs
If you recognize these addiction signs in a loved one, taking action sooner rather than later is crucial. While it may be difficult to address the issue, early intervention can prevent addiction from worsening.
Start with an open, non-judgmental conversation. Express your concerns with compassion rather than blame. If they resist or deny the issue, don’t push—simply reassure them of your support.
If you’re unsure how to proceed, seeking professional guidance is a valuable step. Addiction specialists can offer insights on how to approach the situation and provide recommendations for treatment options that fit your loved one’s needs.
Addiction Looks Different for Everyone
Recognizing substance abuse signs isn’t always straightforward. Signs of an addiction can vary based on the substance used, the duration of addiction, and individual health factors. Not everyone struggling with addiction will exhibit the same symptoms, and some may try to hide their struggles.
It’s essential to look at patterns of behavior rather than focusing on a single warning sign. Subtle shifts in personality, mood, or priorities can indicate a substance abuse problem just as much as obvious physical symptoms. By paying close attention to changes over time, you can better determine whether your loved one needs help.
Addressing Addiction With Compassion
Approaching a loved one about addiction can be an emotional and complex process. Rather than focusing on blame or judgment, emphasize care and concern. Let them know that you’re willing to support them in seeking help when they’re ready.
In many cases, professional addiction treatment is necessary to break the cycle of substance abuse. These specialized programs are designed to address the root causes of addiction while providing personalized support for long-term recovery.
If you or someone you love is struggling, don’t wait to seek help. Support is available, and recovery is possible. Reach out to a trusted addiction treatment provider to explore options for a healthier future.
Connect With Lumina Recovery for Support Today
Recognizing the warning signs of substance abuse is the first step toward getting a loved one the help they need.
At Lumina Recovery, we offer detox programs to help individuals safely manage withdrawal symptoms and begin their recovery journey. For those struggling with both addiction and mental health challenges like anxiety or depression, our dual diagnosis treatment provides comprehensive care to address both conditions simultaneously.
Reach out to Lumina Recovery to explore your options for a healthier, happier future.
Additional Resources
Once you have completed your rehabilitation program at one of our drug and alcohol treatment centers, you should try to surround yourself with people who can encourage you to stay sober. Many people find that support groups are the best source of encouragement. You can find hundreds of support groups and meetings in your community. Our drug addiction treatment centers stress the importance of personal chemical dependency resources, especially when you are new to sobriety. Below are various addiction and mental health resources for people in recovery who want additional support.
Christian Addiction Recovery Resources
Our substance abuse services aren’t limited to specific programs, but rather we believe in the importance of incorporating faith-based programs to promote spiritual healing, like our Faith in Recovery program.
With that said, below are some faith-based addiction recovery resources that could help you in your spiritual healing from addiction:
- Battlefield of the Mind by Joyce Meyer
- Boundaries by Dr. Henry Cloud & Dr. John Townsend
- Christian Families in Recovery: A Guide for Addiction, Recovery, and Intervention Using God’s Tools of Redemption by Robert and Stephanie Tucker
- Club New Life Christian Ministry for Addiction and Recovery
- Lost & Found: Recovery in Christ by Bruce Stanley
- Overcoming Emotional Obstacles through Faith: Navigating the Mind Field by Anthony Acampora, Director of Banyan’s Faith in Recovery Program
- The Case for Christ by Lee Strobel
Mental Health Resources for Recovery
Lumina Recovery consist of both mental health and substance abuse treatment facilities, meaning we offer mental health resources as well as chemical dependency resources. What’s more, addiction often co-occurs with mental illness, making these resources ever more important.
Below are some resources for mental health recovery that can help you or your loved one:
- This Emotional Life video series
- No Kidding, Me 2!! with Joe Pantoliano
- Dare: The New Way to End Anxiety and Stop Panic Attacks by Barry McDonagh
- Pleasure Unwoven: An Explanation of the Brain Disease of Addiction by Kevin McCauley
- Declutter Your Mind: How to Stop Worrying, Relieve Anxiety, and Eliminate Negative Thinking by S.J. Scott and Barrie Davenport
Call Us Today – (877) 716-7515

