What is addiction? Addiction is a chronic, complex, and often misunderstood condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It’s a brain disease that alters functioning and behavior.
For those struggling with a substance use disorder or their loved ones, understanding the stages of the addiction cycle can be a crucial step toward recovery.
Recognizing these stages and risk factors can help individuals identify their patterns and take steps toward recovery.
What Is the Cycle of Addiction?
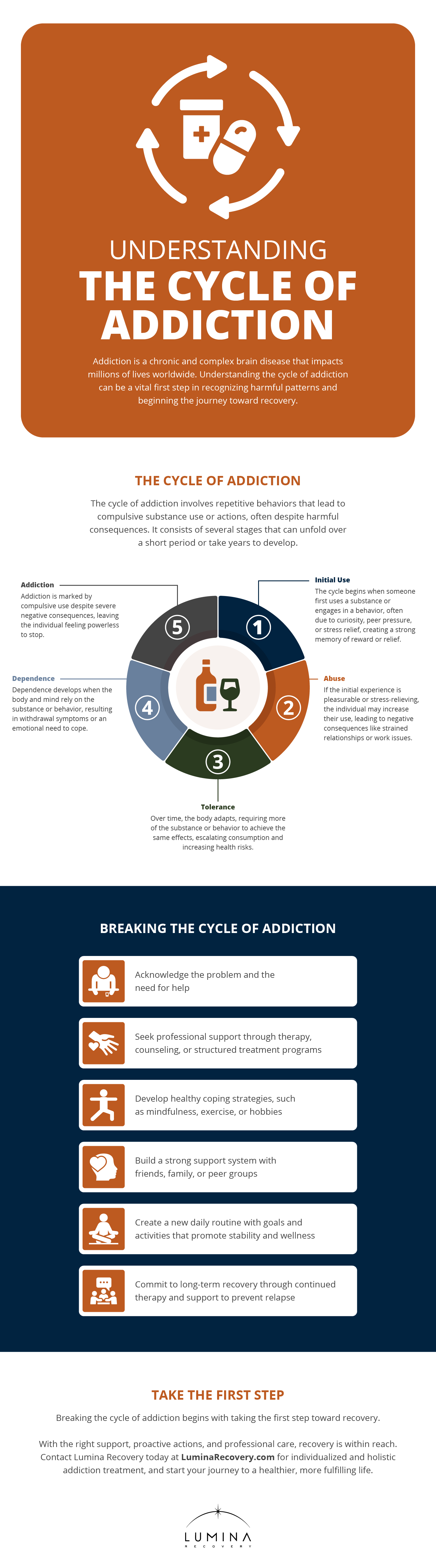
The cycle of addiction refers to the repetitive pattern of behavior that individuals with addiction to drugs or alcohol go through. It’s characterized by a series of stages that can occur in a short period of time or take years to develop.
These stages lead to a compulsive use of substances or engagement in addictive behaviors, despite negative consequences. This cycle can be difficult to break, but understanding its components can help individuals recognize their patterns and take steps toward recovery.
The Stages of the Cycle of Addiction
Addiction is a progressive condition that develops over time, often going unnoticed until it becomes severe. By understanding the specific stages of the cycle of addiction, individuals and their loved ones can better recognize the warning signs and seek help earlier.
1. Initial Use
The cycle often begins with the initial use of a substance or behavior. This might happen due to curiosity, peer pressure, stress relief, or the pursuit of pleasure. During this stage, the individual experiences the effects of the substance or behavior, which can be positive, neutral, or negative.
Individuals find some form of physical or mental reward or relief from the initial use, which can create a powerful memory associated with the substance or behavior.
2. Abuse
If the initial use is perceived as pleasurable or effective in relieving stress, the individual may start using the substance or engaging in the behavior more frequently.
This stage is characterized by increased use and the onset of negative consequences, such as problems at work, school, or in relationships. The individual may start prioritizing the substance or behavior over other activities and responsibilities, leading to substance abuse.
3. Tolerance
As the individual continues to use the substance or engage in the behavior, their body begins to build tolerance. This means they need to consume more of the substance or engage in the behavior more frequently to achieve the same effect. Tolerance can lead to increased consumption and a greater risk of negative consequences.
Tolerance occurs as the brain and body adapt to the presence of the substance. For example, someone who drinks alcohol regularly will need to drink more to feel the same level of intoxication they once did with smaller amounts. This increased consumption can accelerate the onset of more serious health and social problems.
4. Dependence
At this stage, the individual’s body and mind become dependent on the substance or behavior. Dependence can be physical, psychological, or both. Physical dependence means the body has adapted to the substance, and stopping use will result in withdrawal symptoms. Psychological dependence involves a mental or emotional need for a substance or behavior to cope with everyday life.
Physical dependence is characterized by withdrawal symptoms when the substance is not used. These symptoms can vary depending on the substance but often include physical discomfort, pain, and cravings. Psychological dependence is marked by an intense desire to use the substance or engage in the behavior to deal with stress, anxiety, or other emotional issues.
5. Addiction
Addiction is marked by the compulsive use of a substance or engagement in a behavior, despite knowing the negative consequences. The individual may feel powerless to stop and continue using or engaging in the behavior, even when it causes significant harm to their health, relationships, and other areas of life.
At this stage, the individual may have tried to quit multiple times but found themselves unable to do so. The substance or behavior has taken over their life, and they may engage in risky or harmful activities to obtain or use the substance. The negative consequences are severe and pervasive, affecting all aspects of the person’s life.
Breaking the Cycle of Addiction
Breaking the cycle of addiction is challenging, but it is possible with the right support and strategies. Here are some steps to help individuals overcome addiction:
The first step in breaking the cycle of addiction is acknowledging the problem. This can be difficult, as denial is a common part of addiction. However, recognizing that there is an issue and that help is needed is crucial for recovery.
Professional help is often necessary to break the cycle of addiction. This can include therapy, counseling, and support groups. Addiction treatment programs, such as those offered by Lumina Recovery, provide a structured environment and comprehensive support to help individuals plan their recovery and overcome addiction.
Learning healthy coping strategies is essential for dealing with triggers and stressors that contribute to addiction. This can include mindfulness, exercise, and hobbies that provide a positive outlet for emotions and stress.
Having a strong support system of friends, family, and peers who understand the challenges of addiction can make a significant difference in recovery. Support groups and peer counseling can also provide valuable encouragement and accountability.
Establishing a new, healthy routine can help individuals avoid the triggers and habits associated with their addiction. This might involve setting new goals, finding new hobbies, and creating a daily schedule that promotes wellness and stability.
Long-term recovery is a process that requires commitment and effort. Continued participation in therapy, support groups, and healthy activities can help individuals maintain their sobriety and prevent relapse. It’s also important to recognize and address any underlying issues, such as mental health disorders, that may contribute to addiction.
Take the First Steps Towards Recovery With Lumina Recovery
Understanding the cycle of addiction is the first step toward breaking free from its grip. By recognizing the stages and taking proactive steps to seek help, develop coping strategies, and build a support system, individuals can overcome addiction and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
At Lumina Recovery, we are committed to providing the necessary addiction treatment programs to help individuals achieve long-term recovery from a range of addiction types including but not limited to alcohol, prescription medications, and opioids.
If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction, reach out today for the help you need.