
Our Addiction Resources
Navigating the world of addiction and recovery can be overwhelming. We’re here to provide clear, compassionate education and guidance. From practical advice for maintaining sobriety to informational guidance on the long-term effects of substance abuse, our content is a beacon of hope and understanding.
Our Team is Ready are ready to take your call
Call us Today!
or we can call you. Fill out form below
Our Blog
Carfentanil Addiction: How to Recognize and Treat It
Carfentanil is a powerful synthetic opioid that has gained notoriety for its extreme potency and dangerous effects. Understanding this substance, recognizing its signs, and knowing the risks associated with its abuse are crucial steps in addressing this growing problem. Below, we’ll explore carfentanil addiction, its impact, and the available treatments.
What Is Carfentanil?
Carfentanil is a powerful synthetic opioid that is related to but distinct from fentanyl. It was originally developed as a tranquilizer for large animals like elephants. It is approximately 100 times stronger than fentanyl and 10,000 times stronger than morphine. Due to its high potency, even a small amount can be lethal to humans.
This substance is often mixed with other drugs, such as heroin, to increase their effects, which significantly raises the risk of overdose. Because of its potency, carfentanil is not approved for human use and poses a significant public health risk.
Identifying Carfentanil
Carfentanil is usually found in powder form but can also be present in blotter papers, tablets, and even nasal sprays. It is often mixed with other drugs, making it difficult to identify without specialized equipment. Its appearance can vary, but it is typically white or off-white in color.
Law enforcement and health officials use advanced laboratory testing to identify carfentanil, as it cannot be detected by standard drug testing kits used for other opioids. This difficulty in identification makes it an especially unique threat.
Signs and Symptoms of Carfentanil Addiction
Carfentanil addiction can have severe physical effects and lead to significant social and behavioral changes. Recognizing these signs can help in seeking professional rehab before things get worse.
Physical effects of carfentanil include:
- Severe drowsiness or sedation
- Respiratory depression
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pinpoint pupils
- Cyanosis (a bluish tint to the skin, especially around the lips and fingertips, indicating a lack of oxygen)
Long-term carfentanil abuse can lead to numerous health issues, including:
- Chronic respiratory problems
- Cardiovascular issues (increased risk of heart attack and heart disease)
- Neurological damage and cognitive problems
- Extreme dependence and severe withdrawal symptoms
There are also some personal and behavioral red flags that may indicate carfentanil addiction, such as:
- Increased secrecy and withdrawal
- Neglect of responsibilities
- Unusual mood changes
- Deteriorating appearance
- Difficulties in relationships and jobs
- Unexplained financial problems
If you notice any of these signs or symptoms in yourself or someone you care about, it’s crucial to get help from an addiction treatment center as soon as possible.
The High Risk of Carfentanil Overdose
As a powerful synthetic opioid drug designed for animals much larger than humans, the most significant danger of carfentanil abuse is overdose. It takes very little carfentanil to be too much for a human, and overdose can quickly be fatal without immediate emergency intervention. It’s important to recognize the signs of an overdose and take action when they appear.
Symptoms of carfentanil overdose include:
- Severe respiratory depression, where breathing becomes dangerously slow or stops
- Loss of consciousness, with an inability to wake up or respond
- Cold and clammy skin, which feels cold to the touch and may appear pale or bluish
- Seizures, marked by uncontrolled shaking or convulsions
This is a medical emergency that requires immediate help. Call 911 if you notice any of these signs in someone who might have taken even a small dose of carfentanil.
The Dangers of Mixing Carfentanil With Other Substances
Mixing carfentanil with other substances, such as alcohol or other opioids, significantly increases the risk of overdose and death. The combined depressant effects can quickly lead to respiratory failure and other life-threatening conditions.
Getting Help for Carfentanil Addiction

Overcoming carfentanil addiction is challenging to do without help, as it’s a very potent drug with severe withdrawal symptoms. Professional treatment is crucial to ensure the safety and success of recovery. Fortunately, there are a variety of program options available, depending on the patient’s needs.
Medically Supervised Detox
Medical detoxification is the first step, where the body is safely cleansed of the drug under medical supervision. This process helps manage withdrawal symptoms and ensures the patient’s safety. Patients receive 24-hour care to prevent complications and keep them comfortable throughout the process. Medical supervision is absolutely crucial for carfentanil detox, as the withdrawal symptoms of opioids are known to be especially intense.
Residential Treatment
Residential treatment means staying at a facility where you receive constant care and support. This type of treatment involves daily therapy sessions, medical monitoring, and activities to help you recover. Living at the facility keeps you away from triggers and stress, allowing you to focus entirely on getting better.
Partial Hospitalization Program (PHP)
Partial hospitalization programs (PHP) provide a high level of care without requiring an overnight stay. You spend most of the day at the treatment center and return home or to a sober living facility in the evening. PHP offers intensive therapy and medical supervision, helping you transition back into daily life while still receiving substantial support.
Intensive Outpatient Program (IOP)
Intensive outpatient programs (IOP) offer treatment while you continue to live at home or another stable, sober living environment. You attend therapy sessions several times a week, which helps you stay on track while managing daily responsibilities. IOP is a good option for those who need structured support but have commitments like work or family.
Lumina Recovery Specializes in Compassionate Addiction Treatment
At Lumina Recovery, we specialize in providing compassionate and comprehensive care for individuals struggling with carfentanil addiction. Our approach combines evidence-based therapies with holistic treatments to address all aspects of addiction.
We offer a variety of programs and methods, including:
- Individualized Treatment Plans: Each patient receives a tailored treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and circumstances.
- Family Therapy: Involving family members in the recovery process helps rebuild relationships and provides a support system for the patient.
- Aftercare Planning: Our comprehensive aftercare planning ensures patients have the resources and support needed to maintain their recovery after leaving our facility.
At Lumina Recovery, our experienced staff provides a nurturing environment where patients can heal physically, emotionally, and mentally. We understand the challenges of carfentanil addiction and know how to address them for the greatest chances of long-term success.
If you or a loved one is struggling with carfentanil addiction, don’t wait to seek help. Contact Lumina Recovery today to learn more about our opioid treatment programs.

The Dangers of Designer Drugs
Designer drugs, also known as synthetic drugs or new psychoactive substances (NPS), are man-made compounds designed to mimic the effects of traditional illegal drugs such as cocaine, marijuana, or heroin.
These substances are often created in laboratories and sold online, in head shops, or on the street. They are often marketed as legal alternatives to traditional drugs, and labeled as “research chemicals,” “bath salts,” or “plant food” to evade regulatory scrutiny. However, this deceptive marketing masks the significant dangers these substances pose to users.1
The creation of designer drugs involves altering the chemical structure of existing drugs to produce similar effects while attempting to circumvent drug laws. This constant modification makes it difficult for authorities to regulate these substances and for users to understand what they are taking. The results can be unpredictable and highly dangerous, leading to severe health risks, addiction, and even death.
Understanding what designer drugs are, why they are used, and the associated risks is crucial for those struggling with addiction and their loved ones.
List of Designer Drugs
According to the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration, there are seven types of designer drugs, including the following:2
- Cannabinoids: These include synthetic cannabinoids like “spice” or “K2,” which mimic the effects of THC, the active ingredient in marijuana.
- Phenethylamines: This class includes drugs like MDMA (Ecstasy) and 2C-B, which have stimulant and hallucinogenic properties.
- Phencyclidines (or Arylcyclohexylamines): Drugs like PCP and its analogs can cause dissociative and hallucinogenic effects.
- Tryptamines: These include drugs like DMT and psilocybin, which are known for their powerful hallucinogenic effects.
- Piperazines: Often sold as “legal ecstasy,” these drugs have stimulant effects similar to MDMA. Examples include BZP and TFMPP.
- Pipradrol: Stimulants that are structurally similar to methylphenidate. Desoxypipradrol is a common example.
- N-ring Systems: This includes a variety of designer drugs with complex ring structures, such as N-bombs, which are potent synthetic hallucinogens similar to LSD.
Why Are Designer Drugs Used?
Designer drugs are often used for several reasons:
Perceived Safety: Many people believe designer drugs are safer because they are synthetic and often marketed as “legal highs.” The packaging and marketing can give the illusion that these substances are controlled and safe to use. However, this is far from the truth. The lack of regulation means these drugs can be highly dangerous.
Avoiding Detection: One significant reason for the popularity of designer drugs is the desire to avoid detection. Standard drug tests may not detect many designer drugs, making them appealing to individuals who undergo regular screening, such as athletes, employees, or people on probation.
Potency: Designer drugs can be much stronger than their traditional counterparts, offering a more intense experience. For instance, synthetic cannabinoids can be far more potent than natural THC, leading to stronger and often more dangerous effects.
Curiosity and Experimentation: The novelty of new substances can attract individuals looking for unique and intense experiences. The constant development of new designer drugs provides a wide array of options for those eager to experiment.
Accessibility: Designer drugs are often easier to obtain than traditional illegal drugs. They can be purchased online or in some stores, sometimes marketed as bath salts, plant food, or research chemicals, making them more accessible to a broader audience.
Peer Pressure and Social Influence: Social environments, such as parties or clubs, can influence individuals to try designer drugs. Peer pressure and the desire to fit in or enhance social experiences can drive someone to experiment with these substances.
Addiction Potential and Dangers of Designer Drugs

Designer drugs pose significant risks. Their unregulated nature means users often do not know what they are consuming or the potential effects. Here are some key dangers:3
Unpredictable Effects
Designer drugs can cause severe and unexpected reactions. Because their chemical compositions are often unknown, they can lead to dangerous outcomes, including:
- Extreme paranoia, hallucinations, and delusions are common.
- Heart attacks, high blood pressure, and irregular heartbeats can occur.
- Seizures, strokes, and severe agitation are risks.
- High potency and uncertain dosing increase the risk of fatal overdoses.
High Addiction Potential
Many designer drugs have a high potential for addiction. They can lead to physical dependence, meaning the body adapts to the drug and requires it to function normally. Withdrawal symptoms can be severe and include:
- Anxiety, depression, emotional instability, and mood swings.
- Physical discomfort like pain, nausea, and fatigue.
- Intense cravings and the desire to use the drug again.
Physical and Mental Health Risks
The health risks associated with designer drugs are profound. The physical and mental health risks include:
- Some designer drugs can cause long-term damage to organs such as the liver, kidneys, and brain.
- Prolonged use can lead to memory loss, reduced cognitive function, and difficulty concentrating.
- Mood swings, irritability, and long-term emotional disturbances can occur.
- The use of designer drugs can exacerbate underlying mental health conditions or trigger new ones, such as anxiety, depression, and schizophrenia.
Social and Legal Consequences
The use of designer drugs can lead to severe social and legal consequences, including:
- Addiction can strain or break relationships with family, friends, and colleagues.
- The inability to maintain regular employment due to drug use can lead to financial instability.
- Despite their initial legality, many designer drugs are eventually banned, leading to potential legal trouble for users.
Get Support for Designer Drug Addiction With Lumina Recovery
Designer drugs are a serious threat to health and well-being. Their unpredictable effects and high addiction potential make them extremely dangerous. It’s crucial to understand these risks and seek help if you or a loved one is struggling with addiction.
At Lumina Recovery, we are here to support you every step of the way through our wide variety of drug treatment programs, including inpatient and outpatient services.
If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction, reach out to our team of addiction specialists for help today.
Sources:
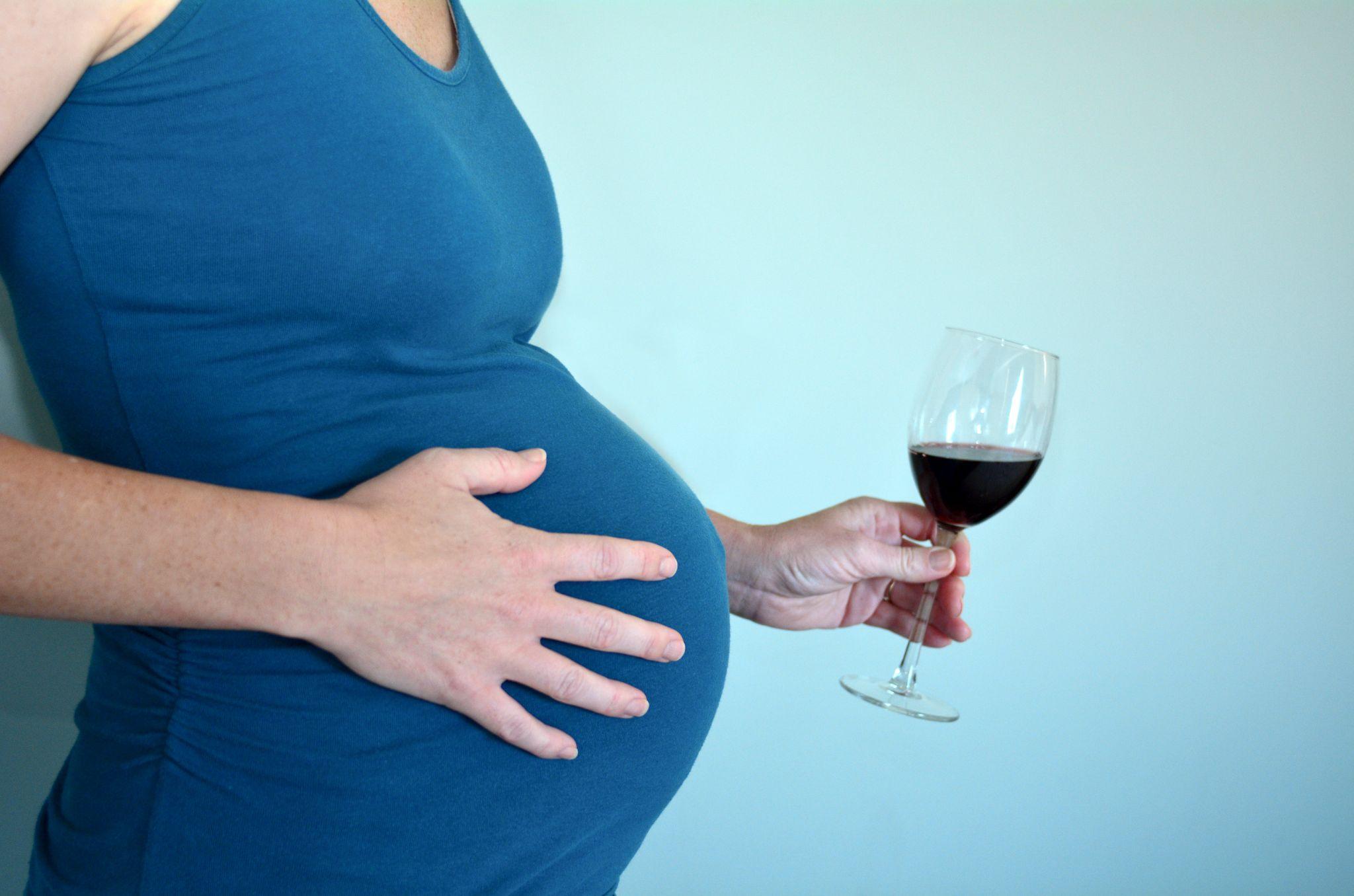

What Is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is a serious condition that affects a child’s development and health due to prenatal alcohol exposure. This syndrome is part of a group of conditions known as fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD).
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism reports that between 1-5% of children in first grade in the United States have FASD, and almost 10% of pregnant women report consuming alcohol during pregnancy.1
While FAS can cause lifelong physical, behavioral, and cognitive problems, it is entirely preventable. Understanding FAS is crucial, especially for those struggling with addiction and their loved ones, as it sheds light on the significant impact of alcohol on unborn children and highlights the challenges faced by pregnant individuals who cannot stop drinking.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Explained
Fetal alcohol syndrome occurs when a developing fetus is exposed to alcohol before birth in the womb. There is no safe amount of alcohol to consume while pregnant because it can cross the placenta, impacting the baby’s brain, heart, and other vital organs.
The severity of FAS varies, but common developmental disabilities and birth defects include distinct facial features, growth deficiencies, and central nervous system problems. Some of the signs and symptoms of fetal alcohol syndrome include:2
Facial Features
- Small head size
- Thin upper lip
- Smooth philtrum (the groove between the nose and upper lip)
- Small eye openings
- Flat nasal bridge
Growth Deficiencies
- Below-average height and weight
- Slow growth before and after birth
Central Nervous System Problems
- Poor coordination and motor skills
- Learning disabilities
- Attention and memory problems
- Hyperactivity
- Poor problem-solving and judgment skills
Behavioral Issues
- Difficulty with social interactions
- Impulsiveness
- Trouble adapting to change or transitions
Other Physical Issues
- Heart defects
- Kidney and bone problems
- Hearing or vision problems
In addition to these effects, children with FAS often face long-term challenges. These can include social difficulties, mental health problems such as anxiety and depression, and an increased risk of substance abuse later in life. Early intervention and supportive therapies can improve outcomes, but the prevention of alcohol exposure during pregnancy remains the most effective strategy for avoiding FAS.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Addiction
From an addiction perspective, understanding why someone who is pregnant might not be able to stop drinking is essential. Addiction is a complex disease that involves physical and psychological dependence on substances. For some, the urge to drink alcohol can overpower the knowledge of its risks, including the potential harm to an unborn child.
Physical Dependence
Physical dependence on alcohol means the body has adapted to the presence of alcohol and needs it to function normally. Withdrawal symptoms can be severe and include anxiety, tremors, seizures, and even life-threatening complications. This physical need for alcohol can make quitting extremely difficult for a pregnant person, even with the awareness of the risks involved.
Psychological Dependence
Psychological dependence includes the emotional and mental aspects of addiction. A person may drink to cope with stress, trauma, or other mental health issues. The emotional grip of addiction can be incredibly strong, making it hard for someone to stop drinking even when pregnant. For many, alcohol becomes a way to self-medicate, creating a cycle of dependency that is difficult to break without professional help.
Co-Occurring Disorders
Many individuals with alcohol addiction also suffer from co-occurring mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, or PTSD. These conditions can exacerbate the need for alcohol as a coping mechanism, making it even more challenging to quit. The interplay between addiction and mental health issues requires comprehensive treatment that addresses both aspects.
Lack of Support
Pregnant individuals with addiction may also lack adequate support systems. They might be afraid to seek help due to stigma or fear of judgment. The shame and guilt associated with drinking during pregnancy can prevent them from reaching out to loved ones or professionals for assistance. This isolation can worsen the addiction and make it harder to seek the necessary help.
What to Do If You’re in This Situation

If you are pregnant and struggling with alcohol addiction, or if you are a concerned loved one of someone who is, there are steps you can take to seek help and support.
- Seek professional help. The first and most crucial step is to seek professional help. This could involve consulting with a healthcare provider, an addiction specialist, or a counselor. Medical professionals can provide a safe and supportive environment to address both pregnancy and addiction.
- Detox under medical supervision. If physical dependence on alcohol is present, a medically supervised detox is essential. Detoxing without medical help can be dangerous for both the pregnant person and the baby. Healthcare providers can offer treatments to manage withdrawal symptoms safely.
- Access prenatal care. Regular prenatal care is vital for monitoring the health of both the mother and the baby. Prenatal visits can also be a time to discuss alcohol abuse and receive guidance on managing addiction during pregnancy.
- Find support groups. Support groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or specialized groups for pregnant women with addiction, can provide a sense of community and shared experience. These groups can offer emotional support and practical advice for managing addiction.
- Engage in therapy. Therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or individual therapy, can be beneficial in addressing the underlying issues related to addiction. Therapy can also help develop coping strategies to avoid alcohol and maintain sobriety.
- Create a support network. Building a strong support network of family and friends who understand the challenges of addiction can make a significant difference. Loved ones can offer emotional support, help with practical needs, and encourage the pregnant person to stay on track with their recovery.
Start Your Journey to Sobriety With Lumina Recovery
Fetal alcohol syndrome is a serious condition that highlights the dangers of alcohol use during pregnancy. For those struggling with addiction, stopping alcohol consumption can be an immense challenge. With the right support and resources, it is possible to overcome addiction and prevent fetal alcohol syndrome.
Lumina Recovery’s programs for alcohol use disorder and dual diagnosis are crucial for anyone looking for addiction support.
Get help and support for alcohol addiction and ensure a healthy future for both mother and baby.
Sources:

Is Addiction Really a Choice?
Addiction is a topic that often sparks intense debate and emotional responses. For those struggling with addiction or their loved ones, understanding the nature of addiction is crucial.
One common question is whether addiction is a choice. This question can shape how we view and treat those affected by addiction. Awareness of the idea of addiction as a choice, the stigma around this concept, and the dangers and consequences of that stigma can help those struggling with a substance use disorder get the help they need.
The Nature of Addiction and Choice
The question of whether addiction is a choice is complex at its core. To address this, we must understand the initial decisions to use drugs or alcohol that may lead to addiction and how these substances affect the brain.
Initial Voluntary Decisions
Initially, the decision to try a substance or engage in a behavior is usually voluntary. People might choose to drink alcohol at a party, experiment with drugs out of curiosity, or start gambling for fun. These initial choices are influenced by various factors, including social pressure, stress, curiosity, or the desire to experience pleasure.1
However, it’s crucial to understand that these initial voluntary actions do not mean that addiction itself is a choice. The path from casual use to addiction involves a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors.
The Transition to Addiction
Once addiction takes hold, it fundamentally alters the brain’s chemistry and function. The brain’s reward system, which is responsible for feelings of pleasure and motivation, is hijacked by the addictive substance or behavior. This hijacking leads to a compulsive cycle of seeking and using the substance despite harmful consequences, also known as the brain disease model of addiction.1
Addiction impacts several brain areas involved in decision-making, self-control, and judgment. These changes can make it extremely difficult for individuals to control their addictive behaviors. The brain’s prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for rational thinking and impulse control, becomes less effective.1
Genetic and Environmental Factors
It’s also important to consider the risk factors of genetics and environmental factors in addiction. Genetics can play a significant role in an individual’s susceptibility to addiction. Certain genetic traits can make a person more likely to develop an addiction to drugs or alcohol when exposed to certain substances or behaviors.1
The Illusion of Choice in Addiction
Changes in the brain caused by addiction lead to a loss of control and a diminished ability to make voluntary choices. This is why many experts argue that while the initial decision to use a substance might be a choice, addiction itself is not. The individual becomes trapped in a cycle of dependency that is incredibly difficult to break without help.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse defines addiction as “a chronic disease characterized by drug seeking and use that is compulsive, or difficult to control, despite harmful consequences.”1
Recognizing this distinction is crucial. It shifts the perspective from seeing addiction as a moral failing to understanding it as a medical condition that requires treatment and support. This understanding can help reduce the stigma and promote a more compassionate approach to those struggling with addiction.
The Stigma of Choice and Its Consequences
The idea that addiction is a choice contributes significantly to the stigma surrounding it. This stigma manifests as the belief that those with a drug or alcohol addiction are weak-willed, morally flawed, or simply making poor choices. The consequences of this stigma are far-reaching and deeply damaging.
Moral Judgments and Internalized Stigma
When addiction is viewed as a choice, it leads to harsh moral judgments. People with addiction are often labeled as irresponsible, lazy, or lacking in self-discipline. Such judgments foster a lack of empathy and understanding from others, including family members, friends, employers, and healthcare providers.
This external stigma often becomes internalized, causing those with addiction to view their struggle as a personal failure. They may feel intense worthlessness, shame, and guilt. When individuals see their addiction as a moral failing rather than a medical condition, they are less likely to seek help, fearing judgment and rejection from others.
Social Isolation and Barriers to Treatment
Stigma can lead to social isolation for those with addiction. Friends and family members might distance themselves, making it difficult for individuals to maintain relationships or build new ones.
Stigma creates significant barriers to treatment for addiction. Individuals may avoid seeking help due to fear of being judged or labeled. This avoidance can delay or prevent access to essential treatment from medical professionals and support services, prolonging the addiction and increasing the risk of severe health consequences.
Inadequate Healthcare and Mental Health Impact
Healthcare providers may hold biased views about addiction, leading to inadequate care. Some might dismiss the severity of the addiction, offer insufficient treatment options, or fail to address the underlying issues contributing to the addiction. This can result in a cycle where individuals with addiction receive substandard care, reinforcing their struggle and reducing their chances of recovery.
The mental health impact of stigma is profound. Individuals with addiction may experience increased anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues due to constant judgment and discrimination. This can create a vicious cycle, where mental health struggles contribute to substance use, and substance use worsens mental health.
Overdose and Fatalities
One of the most severe consequences of stigma is the increased risk of overdose and fatalities. When individuals are afraid to seek help or are unable to access effective treatment, they are at higher risk of using substances in dangerous ways. Overdoses can occur when individuals use substances alone, without the possibility of receiving immediate medical assistance.
How to Get Help for Addiction

If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction, seeking help is a crucial step toward recovery. Here are the key steps to get the support you need:
Acknowledge the problem. Recognize that addiction is a medical condition that requires treatment. Acknowledging the problem is the first step toward seeking help.
Reach out for support. Talk to trusted family members, friends, or healthcare providers about your struggle. Having a support system can provide emotional backing and practical assistance.
Explore treatment options. Treatment can include inpatient or outpatient programs, therapy, medication, and support groups. Research and choose a treatment plan that best suits your needs.
Join support groups. Groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA) provide peer support and a sense of community. These groups can offer guidance, encouragement, and accountability.
Commit to ongoing treatment. Recovery is an ongoing process. Regularly attend therapy sessions, support groups, and follow-up appointments to maintain your progress and address any challenges.
Get Help for Addiction With Lumina Recovery
Addiction is a complex disease that affects millions of people worldwide. The initial choice to use a substance or engage in a behavior does not mean that addiction itself is a choice. Understanding this can help reduce the stigma surrounding addiction. By changing our perceptions and providing effective treatment and support for substance abuse, we can help those struggling with addiction find a path to recovery.
Lumina Recovery offers addiction treatment programs for various types of addiction as well as dual diagnosis services to treat the whole individual on their unique journey to recovery.
Reach out today to begin the journey toward a healthier, addiction-free life.
Sources:
Your Guide to Dihydrocodeine Addiction
Dihydrocodeine is a strong painkiller often prescribed to treat moderate to severe pain. While it can be very effective, it also has a high potential for addiction. This guide will help you understand dihydrocodeine, the risks of addiction and overdose, and the treatment options available.
What Is Dihydrocodeine?
Dihydrocodeine is a semi-synthetic opioid derived from codeine. Doctors commonly prescribe it to help manage moderate to severe pain caused by surgeries, injuries, or chronic conditions. Dihydrocodeine works by blocking pain signals in the brain and spinal cord, which provides pain relief and a sense of well-being. This medication is available in both tablet and liquid forms and is usually taken by mouth.
Is Dihydrocodeine Addictive?
Yes. While dihydrocodeine is very effective for managing pain, it is an opioid medication that can easily cause dependence if not used correctly. It’s important to understand what dihydrocodeine is and how it works to be aware of the potential risks associated with its use.
Dihydrocodeine Addiction
Dihydrocodeine addiction can start quickly, especially if the drug is used more than prescribed. Even with correct use, regular intake can lead to tolerance, where the body needs more of the drug to feel the same effects. This can lead to dependence and addiction.
Dihydrocodeine has a variety of effects on the body, including:
- Reduced pain
- Feelings of euphoria
- Drowsiness
- Constipation
- Respiratory depression (slow breathing)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion and cognitive problems
When misused for a long time, dihydrocodeine can have even more severe impacts, such as:
- Liver damage
- Chronic respiratory problems
- Mental health issues (depression, anxiety)
- Steadily increasing risk of overdose
Behavioral and Social Red Flags
In addition to the physical symptoms, dihydrocodeine addiction also causes a variety of changes to a person’s moods and behaviors.
Signs that someone may be addicted to dihydrocodeine include:
- Taking higher doses than prescribed
- Feeling unable to stop using the drug
- Withdrawal symptoms (anxiety, sweating, nausea)
- Neglecting responsibilities
- Continuing use despite negative consequences
- Isolating from family and friends
- Changes in mood and behavior (mood swings, depression, irritability)
- Problems in relationships and at work
- Financial and legal problems
- Reduced quality of life and well-being
Dihydrocodeine Overdose
Opioid medications are known for having an especially severe risk of overdose due to their powerful, potent effects. An overdose occurs when a person takes too much dihydrocodeine, leading to life-threatening symptoms like difficulty breathing, extreme drowsiness, and loss of consciousness. Overdose requires immediate medical attention.
The risk for dihydrocodeine overdose is extremely high, especially when combined with other substances (a practice known as polydrug use). When dihydrocodeine is mixed with other substances, the combined effects are unpredictable and can create entirely new dangers. Using it with alcohol or sedatives, for example, can severely depress the central nervous system, making it easier to stop breathing.
In addition to polydrug use, other factors can increase the risk of overdose, including:
- Taking increasingly higher doses
- Underlying health conditions
- Having a history of other substance abuse
- Being dehydrated or malnourished
Preventing and Addressing Overdose
If you or someone you know is addicted to dihydrocodeine, the best way to prevent an overdose is to never start misusing the medication. However, if misuse has already begun, it’s crucial to seek professional treatment immediately to prevent the problem from worsening. Getting help early can significantly reduce the risk of severe health complications and overdose. It’s also important to recognize the symptoms of an overdose and be ready to take action and call 911.
In addition to seeking treatment, having NARCAN (naloxone) on hand can be a lifesaving measure. NARCAN is an over-the-counter medication that can temporarily reverse the effects of an opioid overdose, buying valuable time until first responders arrive. If you or someone you care about is at risk, consider purchasing NARCAN from a local pharmacy and keeping it in a safe, accessible place. Knowing how to use it and acting quickly in the event of an overdose can make the difference between life and death.
Getting Treatment for Dihydrocodeine Addiction

Professional treatment is crucial for overcoming dihydrocodeine addiction. It provides medical supervision, therapy, and support needed to recover. Treatment options vary based on individual needs and the severity of the addiction.
Inpatient Treatment
Residential inpatient treatment involves staying at a facility where patients receive around-the-clock care and support. This intensive treatment helps manage withdrawal symptoms and provides a structured environment for recovery.
Partial Hospitalization Programs
Partial hospitalization programs (PHP) offer a middle ground between inpatient and outpatient treatment. Patients attend treatment sessions during the day and return home or to a sober living facility at night. This level of care is ideal for those needing more support than outpatient but not requiring full-time residential care.
Intensive Outpatient Programs
Intensive outpatient programs (IOP) are more flexible than inpatient programs and PHPs. Patients are able to live at home or in a sober living facility and continue their work and/or schooling while attending therapy sessions several times a week. This option provides flexibility for those who cannot commit to inpatient treatment but still need substantial support.
Lumina Recovery Offers Comprehensive Treatment for Lasting Sobriety
Choosing Lumina Recovery means accessing a comprehensive treatment program designed for lasting sobriety. We specialize in opioid addiction treatment, providing personalized care tailored to each individual. Our dedicated team supports clients through every step of their recovery journey, from detox to aftercare.
We offer a variety of effective, evidence-based methods, including (but not limited to):
- Family Therapy: We involve family members in the recovery process, helping to rebuild trust and improve communication within the family unit.
- Dual-Diagnosis Care: Our dual-diagnosis care addresses both addiction and any underlying mental health issues, ensuring a holistic approach to treatment.
- Medication-Assisted Treatment: We use medications to help manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings, making the recovery process more manageable.
- Aftercare Support: Our aftercare support provides ongoing assistance and resources to help clients maintain their sobriety long after the initial treatment has ended.
If you or a loved one needs help with dihydrocodeine addiction, contact Lumina Recovery today and start your journey with opioid addiction treatment.

Demerol Addiction Overview
Demerol, also known generically as meperidine, is a prescription painkiller used to treat moderate to severe pain. While effective for pain management, Demerol carries a high risk of addiction. Understanding Demerol addiction, its side effects, and how to get help is crucial for those affected. This guide will provide a comprehensive look into Demerol addiction and the steps to recovery.
What Is Demerol?
Demerol is a pain medication prescribed by doctors to treat moderate to severe pain. It belongs to a class of drugs called opioids, which work by changing how the brain and nervous system respond to pain. Demerol can be prescribed as a pill, syrup, or injectable solution, depending on the patient’s needs and preferences.
Is Demerol Addictive?
While Demerol can be very effective for short-term pain relief, it is not typically recommended for long-term use due to its high potential for addiction. Demerol creates a pleasant relaxation and euphoria, which can cause people to want to use it for longer or in greater amounts than prescribed. Unfortunately, this can quickly lead to a dependency.
Demerol Side Effects and Symptoms of Abuse
Demerol can have beneficial effects on the body when used as intended and under medical supervision. However, misusing Demerol can lead to dangerous effects and an ongoing addiction. Recognizing the effects and signs of abuse can help in seeking timely help.
In the short term, the effects of Demerol on the body include:
- Pain relief
- Relaxation
- Drowsiness or sedation
- Euphoria or a feeling of well-being
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation
Some of these short-term effects are what make Demerol such an effective drug when used properly in a healthcare setting. With long-term misuse, however, Demerol can become a dangerous addiction with severe repercussions.
Long-term effects of Demerol abuse may include:
- Chronic respiratory problems
- Ongoing constipation and gastrointestinal issues
- Constant fatigue
- Organ damage
- Increased risk of infections
- Cognitive impairment
- Mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety
- Sleeping problems
- Cardiovascular issues; increased risk of heart attack and stroke
- Physical dependence and severe withdrawal symptoms
Behavioral Signs of Addiction
In addition to the physical and mental effects, someone who is abusing Demerol can behave in unusual ways.
Watch for these additional red flags for Demerol addiction:
- Needing more of the drug to feel the same effects (tolerance)
- Constantly thinking about obtaining and using Demerol
- Ignoring responsibilities and activities once enjoyed
- Mood swings and irritability
- Changes in social behavior, such as isolation or secretive actions
- Financial problems due to spending money on the drug
- Neglecting personal hygiene and appearance
The Dangers of Combining Demerol With Other Drugs
Combining Demerol with other substances can enhance the effects of both, sometimes creating new and more dangerous effects. This practice, known as polydrug use, significantly increases the risks and side effects.
Here’s how different commonly combined drugs can interact with Demerol:
- Alcohol: Alcohol can amplify the sedative effects of Demerol, leading to extreme drowsiness, respiratory depression, and even coma.
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., Xanax, Valium): These drugs, like Demerol, are central nervous system depressants. Their combined effects can lead to severe sedation, respiratory failure, and death.
- Other Opioids (e.g., Oxycodone, Heroin): Using multiple opioids together greatly increases the risk of overdose, potentially causing severe respiratory depression and death.
- Stimulants (e.g., Cocaine, Methamphetamine): Mixing stimulants with Demerol can create a dangerous push-pull on the heart and respiratory system, leading to severe, unpredictable cardiovascular problems.
Polydrug use creates highly unpredictable results. The effects can vary greatly, and these unpredictable interactions can increase the risk of severe harm and make it harder to quit. If you are living with a Demerol addiction, it’s absolutely critical that you avoid other substances to reduce your risks.

How to Get Help for Demerol Addiction
Seeking Demerol addiction treatment is essential for long-lasting recovery. Overcoming addiction requires comprehensive care, addressing both the physical dependence and the underlying psychological issues. At Lumina Recovery, we offer a range of services designed to support you at every stage of your recovery journey.
Medically Supervised Detox
Medically supervised detox is a crucial first step for anyone addicted to Demerol, as opioid withdrawal can be extremely difficult and dangerous without professional help. Medical staff can provide medications and support to ease withdrawal symptoms, ensuring a safer detox process. During detox, professionals monitor vital signs and manage symptoms to prevent complications. This phase is vital to cleanse the body of Demerol safely and prepare for further treatment.
Professional Treatment Options
After detox, ongoing treatment is key to long-term recovery. At Lumina Recovery, we offer personalized treatment plans that address the root causes of addiction. Our approach includes various therapy and counseling options, as well as holistic care, to support lasting sobriety.
Inpatient Treatment
Inpatient treatment involves staying at our facility where you will receive round-the-clock care. This program is ideal for those with severe addictions or those who need a structured environment to focus on recovery without external distractions. Inpatient treatment typically includes individual therapy, group therapy, and various therapeutic activities.
Partial Hospitalization Program (PHP)
Partial hospitalization offers structured treatment during the day and the ability to return home or to a sober living facility at night. This program includes medical monitoring, intensive therapy, and various therapeutic activities. PHP is ideal for those who need significant support but also have a stable, sober living environment.
Intensive Outpatient Program (IOP)
Intensive outpatient care is a step down from inpatient treatment and partial hospitalization programs (PHP), providing intensive care while allowing you to live at home or in a sober living facility. It involves several hours of therapy and counseling each week, focusing on relapse prevention and coping strategies. IOP is designed for individuals who need more support than standard outpatient treatment but do not require 24-hour supervision.
Get Compassionate Demerol Addiction Treatment at Lumina Recovery
Overcoming Demerol addiction is possible with the right support and treatment. At Lumina Recovery, we’re dedicated to helping individuals break free from addiction and reclaim their lives. Our experienced team provides compassionate care and effective treatment strategies.
If you or someone you love is struggling with Demerol addiction, don’t wait to seek help. Contact Lumina Recovery today to start on the path to recovery.

Dry Drunk Syndrome: What It Is & How to Cope
Sobriety is a challenging journey that goes beyond just abstaining from alcohol. For many, achieving sobriety is just the first step. One phenomenon that can occur after quitting drinking is known as “dry drunk syndrome.” Understanding what this is and how to cope with it can be crucial for long-term recovery.
What Is Dry Drunk Syndrome?
Dry drunk syndrome refers to a condition where individuals who have quit drinking continue to exhibit the same negative behaviors and thought patterns associated with alcohol use disorder (AUD). Even though they are not consuming alcohol, their mindset and actions can mirror those of their drinking days. This can hinder their recovery and lead to significant emotional and psychological distress.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Dry Drunk Syndrome?
Dry drunk syndrome can manifest in various ways, impacting both the individual and their relationships. Recognizing these signs is the first step toward addressing the issue.
- Irritability and Anger: Persistent frustration and anger, often directed at oneself or others.
- Resentment: Holding onto grudges and feeling envious of others who can drink without consequences.
- Negative Thinking: Pervasive pessimism and a tendency to focus on the negative aspects of life.
- Complacency: Lack of motivation to continue personal growth and recovery efforts.
- Self-Pity: Feeling sorry for oneself and believing they are a victim of their circumstances.
- Blame Shifting: Refusing to take responsibility for one’s actions and blaming others for personal problems.
- Isolation: Withdrawing from social interactions and support networks.
- Dishonesty: Lying about feelings, situations, or intentions to oneself or others.
How to Cope With Dry Drunk Syndrome
Coping with dry drunk syndrome requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying emotional and psychological issues. Here are some effective strategies to manage this condition and begin moving toward a healthier way of living.
1. Develop Self-Awareness
Understanding and acknowledging the existence of dry drunk syndrome is pivotal. Self-awareness can help you identify negative patterns and behaviors. Journaling and mindfulness practices can be beneficial tools in developing this awareness.
2. Build a Support Network
Connecting with others who understand your journey can provide much-needed support and encouragement. This can include support groups, sober friends, and family members who support your recovery.
3. Practice Healthy Living
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can have a positive impact on your mental and emotional well-being. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation.
4. Set Goals
Setting and working towards personal goals can provide a sense of purpose and direction. These goals should be realistic and achievable, helping to build confidence and a sense of accomplishment.
5. Stay Committed to Sobriety
Maintaining sobriety requires ongoing effort and dedication. Regularly attending support group meetings, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), can provide ongoing motivation and accountability.
Getting Help for Dry Drunk Syndrome
Professional help is often necessary to effectively address dry drunk syndrome. It’s important to understand that addiction recovery involves much more than just ending substance use. Even if you are no longer actively drinking, you can still seek treatment to heal the underlying issues that continue causing problems in your life.
Therapists and counselors who specialize in addiction recovery can provide the expertise and support needed to navigate this challenging phase of sobriety.
Inpatient Treatment Programs
Even if you’ve finished treatment or aren’t drinking now, keeping the mindset and behaviors of an alcoholic can cause distress and increase the risk of relapse. If you need strong support or fear a relapse, inpatient treatment can help. It provides a focused recovery environment where you can fully concentrate on your sobriety, no matter where you’re starting from.
Outpatient Treatment Programs
Outpatient treatment programs offer flexibility for individuals who need to maintain their daily responsibilities while receiving treatment. These programs vary in intensity and can include partial hospitalization programs (PHP) and intensive outpatient programs (IOP). Outpatient treatment provides access to services on a schedule that allows you to continue working, attending school, or caring for family. It’s a practical option for ongoing support and relapse prevention.
Individual Therapy
Individual therapy is a common part of both inpatient and outpatient programs. It offers a one-on-one setting where you can explore your personal experiences, thoughts, and feelings with a trained therapist. This type of therapy is highly personalized, allowing for deep exploration of the issues underlying your dry drunk syndrome.
Group Therapy
Another common element of treatment programs, group therapy provides a supportive environment where individuals facing similar challenges can share their experiences and learn from one another. This form of therapy helps reduce feelings of isolation and fosters a sense of community. It allows participants to gain different perspectives on their issues and develop new strategies for coping with dry drunk syndrome. Peer support is a powerful tool in the recovery process.
Lumina Recovery Offers Specialized Help

At Lumina Recovery, we offer comprehensive treatment programs tailored to meet the unique needs of individuals at all stages of recovery. Our approach combines evidence-based therapies with holistic practices to support long-term sobriety, whether you’re just getting started or have been through treatment before.
Therapies We Use
We offer a variety of therapies to address the emotional, psychological, and physical aspects of addiction recovery. Our therapies include (but are not limited to):
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)
- Family therapy
- Hypnotherapy
- Medication-assisted treatment (MAT)
Our Treatment Programs
Our comprehensive treatment programs are designed to address the diverse needs of our clients. Whether you’re looking for intensive outpatient programs, partial hospitalization programs, or residential treatment, we have options to support your recovery journey.
Help for Co-Occurring Disorders
Many individuals struggling with dry drunk syndrome may also have co-occurring mental health disorders. In our dual diagnosis program, we tackle both the addiction and any co-existing mental health issues simultaneously, ensuring comprehensive care and support.
Start Your Sobriety Journey Today at Lumina Recovery
Taking the first step towards recovery can be daunting, but you don’t have to do it alone. At Lumina Recovery, we are committed to providing the support and resources you need to achieve lasting sobriety.
Contact us today to start your journey towards a healthier, happier life.

Is It Safe to Detox at Home?
Detoxification, commonly known as detox, is the first step towards recovery from addiction. It involves stopping drinking or using substances and removing them from the body. While detox is a critical phase in the journey to sobriety, it is also one of the most challenging and risky stages.
Many people believe it is safe to detox at home, thinking it to be a more private and cost-effective option. However, detoxing at home can be fraught with dangers that can put one’s health and life at risk. Understanding what it means to detox at home, the potential dangers associated with it, and why doctors recommend medically supervised detox will aid in long-lasting recovery.
What It Means to Detox at Home
Detoxing at home refers to the process of attempting to withdraw from alcohol or drugs and cleanse the body of these substances without the supervision of trained professionals.
Detox includes abruptly stopping the use of the substance or gradually reducing the intake over time. Individuals may use home remedies, over-the-counter medications, or even herbal supplements in an attempt to alleviate withdrawal symptoms.
7 Potential Dangers Associated With Detoxing at Home
Detoxing at home can seem like a viable option due to its privacy and cost-effectiveness, but it comes with significant risks that can jeopardize one’s health and safety. Understanding these potential dangers is crucial for making an informed decision about the detox process.
1. Severe Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms occur when the body reacts to the sudden absence of a substance it has become dependent on. Detox symptoms can vary widely depending on the substance used, the duration and severity of the addiction, and the individual’s overall health. Common withdrawal symptoms include:1
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances if not properly managed.
- Tremors and Seizures: Particularly common in alcohol and benzodiazepine withdrawal, seizures can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
- Hallucinations and Delirium: These severe symptoms, often associated with alcohol withdrawal, can cause extreme confusion and agitation, posing risks to the individual and those around them.
- Severe Anxiety and Depression: The emotional toll of withdrawal can be intense, leading to panic attacks, severe depression, and even suicidal thoughts.
2. Risk of Relapse
The intense discomfort of withdrawal symptoms often leads individuals to relapse. The urge to use the substance again to alleviate the suffering can be overwhelming. Relapse during detox is particularly dangerous because it can lead to binge use, increasing the risk of overdose and further entrenching the addiction.
3. Lack of Emotional and Psychological Support
Detoxing from addictive substances involves significant emotional and psychological challenges. The absence of professional support can leave individuals feeling isolated and overwhelmed. Emotional support is crucial during detox to help individuals cope with the psychological aspects of withdrawal, such as:
- Depression: The brain’s chemistry changes during detox, which can lead to deep depression. Without support, this can become a major obstacle to recovery.
- Anxiety: Withdrawal can cause intense anxiety and panic attacks, which are difficult to manage alone.
- Mood Swings: Emotional instability is common, and without support, it can lead to impulsive decisions, including physical and emotional relapse.
4. Potential Medical Complications
Certain substances pose specific medical risks during withdrawal that require immediate and skilled medical intervention:
- Alcohol Withdrawal: Can lead to delirium tremens (DTs), a severe form of withdrawal that includes sudden and severe mental or nervous system changes as well as alcohol withdrawal seizures. DTs can cause shaking, confusion, high blood pressure, fever, and hallucinations, which can be fatal if untreated.2
- Opioid Withdrawal: Though not typically life-threatening, opioid withdrawal can cause severe dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and increased heart rate, all of which can lead to complications without medical intervention.3
- Benzodiazepine Withdrawal: Abruptly stopping benzodiazepines can lead to seizures, psychosis, and even death.4
5. Inadequate Pain Management
Withdrawal symptoms can be extremely painful, and managing this pain is challenging without professional help. At home, individuals lack access to medications and therapies that can safely alleviate these symptoms. This often leads to:
- Self-Medication: Individuals may use over-the-counter drugs, alcohol, or other substances in an attempt to manage withdrawal pain, which can lead to complications or new dependencies.
- Unproven Remedies: Some may turn to unverified home remedies that can be ineffective or harmful, exacerbating the withdrawal process.
6. Unsupervised Medical Conditions
Many individuals with substance use disorders have underlying medical conditions that can complicate detox. Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or mental health disorders require careful monitoring and management during detox. Without medical supervision, these conditions can worsen, leading to serious health crises.
7. Inconsistent Detox Environment
The home environment may not be conducive to a successful detox. Triggers and stressors that contributed to the addiction can still be present, making it difficult to focus on recovery. An unsupportive or stressful home environment can increase the likelihood of relapse and make the detox process more challenging.
Why Doctors Recommend Medically Supervised Detox

Given the risks associated with detoxing at home, medical professionals strongly advocate for medically supervised detox programs as the safest way to detox. These programs offer a safe and structured environment where individuals can detox under the care of trained healthcare providers.
Comprehensive Medical Support
In a medically supervised detox program, individuals have access to 24/7 medical care. Healthcare providers can monitor vital signs, manage withdrawal symptoms with appropriate medications, and intervene promptly if complications arise. This ensures that the detox process is safe and comfortable.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Medical detox programs often include counseling and support services to address the emotional and psychological aspects of detox. Trained therapists and counselors provide support, coping strategies, and encouragement, helping individuals navigate the challenges of detox and prepare for the next steps in their recovery journey.
Lower Risk of Relapse
The structured environment of a detox facility reduces the risk of relapse. With constant supervision and support, individuals are less likely to succumb to the urge to use substances to alleviate withdrawal symptoms. This helps break the cycle of addiction and sets the stage for sustained recovery.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Medically supervised detox programs offer personalized treatment plans tailored to the individual’s needs. Healthcare providers assess the individual’s medical history, the substance of abuse, and the severity of the addiction to develop a customized detox plan. This personalized approach enhances the effectiveness of the detox process and reduces the risk of complications.
Safe Transition to Ongoing Treatment
Detox is just the first step in the recovery process. Medically supervised detox treatment programs ensure a smooth transition to ongoing treatment, such as inpatient or outpatient treatment facilities, counseling, and support groups. This continuum of care is essential for achieving long-term sobriety and preventing relapse.
Ensure a Safe and Effective Detox With Lumina Recovery
While the idea of detoxing at home may seem appealing, it comes with significant risks and dangers. Medically supervised detox programs offer a safer and more effective alternative, providing comprehensive medical care, emotional support, and personalized treatment plans.
Lumina Recovery provides detox services and medically assisted treatment (MAT) that ensure safety and support throughout the detoxification process. For those struggling with addiction and their concerned loved ones, seeking professional help is the best way to ensure a safe detox and a successful path to recovery.
Take the first step towards a safer and healthier recovery with professional help.
Sources:
Drug Paraphernalia: A Guide for Loved Ones
Discovering that a loved one might be using drugs is a distressing and overwhelming experience. One of the signs that can indicate drug use is the presence of drug paraphernalia. These items are often used to consume, produce, or conceal drugs.
Understanding what to look for can help you identify potential issues early and take the necessary steps to provide support. Lumina Recovery aims to educate concerned loved ones about the various types of drug paraphernalia, so you can better understand and address the situation.
What Is Drug Paraphernalia?
According to federal law, drug paraphernalia is defined as “any equipment, product or material of any kind which is primarily intended or designed for use in manufacturing, compounding, converting, concealing, producing, processing, preparing, injecting, ingesting, inhaling, or otherwise introducing into the human body a controlled substance.”1
Possession of drug paraphernalia is also against the law. The U.S. Code Title 21 Section 863 states that there are drug paraphernalia laws making it illegal for anyone to sell, transport via mail or interstate commerce, or import or export drug paraphernalia.2
Types of Drug Paraphernalia
1. Smoking Devices
Pipes: These can be made from a variety of materials, including metal, glass, wood, acrylic, stone, plastic, and ceramic. They may or may not have a screen, punctured metal bowl, or hashish head. Pipes can be used to smoke various substances, including marijuana, methamphetamine, and crack cocaine. They may look similar to tobacco pipes but often have a more elaborate design.
Bongs: Also known as water pipes, bongs are used to smoke marijuana. They filter smoke through water before inhalation. Bongs can vary in size and are typically made of glass, plastic, or ceramic.
Vaporizers: These devices heat substances to create vapor instead of smoke. They are commonly used for marijuana and nicotine. Vaporizers can look like pens or USB drives, making them harder to identify.
Bowls: Bowls are objects used to hold burning material for smoking and come in various shapes and sizes, tailored to the substance being used. Marijuana is often smoked from a colorful bowl with an elongated mouthpiece.
Aluminum Foil: Aluminum foil is often utilized to smoke various drugs, including cocaine and heroin. It is particularly prevalent for smoking prescription painkillers. Smoking these substances allows the drug to enter the bloodstream more quickly than ingesting them, making this method more attractive to users.
2. Injecting Equipment
Needles and Syringes: These are used to inject drugs like heroin, cocaine, and methamphetamine directly into the bloodstream. Finding needles or syringes is a clear sign of intravenous drug use.
Tourniquets: These are used to make veins more visible and easier to inject into. Items like belts, rubber tubing, or shoelaces can be used as makeshift tourniquets.
Cookers: These are small containers used to heat and dissolve drugs before injection. Common items repurposed as cookers include bottle caps and spoons.
Bandanas, Spoons, Bottle Caps, and Belts: These items frequently signal intravenous (IV) drug use. Although various substances can be injected intravenously, opiates are the most commonly used in this manner.
3. Snorting Tools
Straws and Tubes: Small, often cut-down straws or tubes are used to snort drugs like cocaine or heroin. They can be made from plastic or metal.
Razor Blades and Cards: These are used to chop drugs into fine powder for snorting. Razor blades, credit cards, or ID cards are often used for this purpose.
Rolled-Up Dollar Bills, Straws, and Pens: Pens can be taken apart, and straws can be cut down for the purpose of snorting drugs. Substances that are often crushed and snorted include, heroin, cocaine, methamphetamine, ecstasy, and various pills.
4. Concealment Devices
Stash Cans: These look like everyday items (soda cans, hairbrushes) but are hollowed out to hide drugs or paraphernalia. They can be surprisingly convincing and difficult to spot.
Fake Containers: Similar to stash cans, these are designed to look like normal objects, such as books or household products, with hidden compartments.
Clothing: Some clothing items have secret pockets or compartments to hide drugs or paraphernalia. Bags and backpacks may also have hidden sections.
5. Other Common Paraphernalia
Rolling Papers and Blunts: Used to roll and smoke marijuana. Blunts are often cigars that have been hollowed out and filled with marijuana.
Grinders: These are used to break down marijuana buds into a finer consistency for smoking. Grinders can be made from metal, plastic, or wood.
Scales: Small digital scales are used to measure drug quantities. They are often pocket-sized and highly portable.

What to Do If You Find Paraphernalia
If you find any of these items, it is crucial to approach the situation with care and sensitivity.
Try to communicate. Have an open and honest conversation with your loved one. Express your concerns without judgment. Use “I” statements to avoid sounding accusatory, such as “I am worried about you because I found these items.” Prepare for the conversation by choosing a calm time and place where you can talk without interruptions.
Listen actively. During the conversation, listen more than you speak. Give your loved one the opportunity to explain their side. Show empathy and understanding, as this can help build trust and openness.
Seek support. Reach out to professionals who can provide guidance and support. This can include counselors, addiction specialists, and support groups for families. Professional guidance from addiction treatment centers can help you navigate the complexities of addiction and provide resources for both you and your loved one.
Offer help. Encourage your loved one to seek treatment. Offer to help them find resources and accompany them to appointments if they are willing. Show them that you are there to support them through the recovery process.
Stay patient and hopeful. Recovery is a long and often difficult journey. There may be setbacks along the way, but staying patient and hopeful can make a significant difference. Celebrate small victories and continue to offer your support.
Support Your Loved One’s Recovery With Lumina Recovery
Recognizing drug paraphernalia is an essential step in addressing potential substance abuse issues. Remember to approach the situation with empathy and seek professional help to navigate this challenging time. Your support can make a significant difference in their journey toward recovery.
Lumina Recovery offers specialized programs tailored to address a wide array of drug types, ensuring holistic and individualized treatment for each client.
Reach out today to make a difference in their journey towards a healthier, drug-free life.
Sources:
Additional Resources
Once you have completed your rehabilitation program at one of our drug and alcohol treatment centers, you should try to surround yourself with people who can encourage you to stay sober. Many people find that support groups are the best source of encouragement. You can find hundreds of support groups and meetings in your community. Our drug addiction treatment centers stress the importance of personal chemical dependency resources, especially when you are new to sobriety. Below are various addiction and mental health resources for people in recovery who want additional support.
Christian Addiction Recovery Resources
Our substance abuse services aren’t limited to specific programs, but rather we believe in the importance of incorporating faith-based programs to promote spiritual healing, like our Faith in Recovery program.
With that said, below are some faith-based addiction recovery resources that could help you in your spiritual healing from addiction:
- Battlefield of the Mind by Joyce Meyer
- Boundaries by Dr. Henry Cloud & Dr. John Townsend
- Christian Families in Recovery: A Guide for Addiction, Recovery, and Intervention Using God’s Tools of Redemption by Robert and Stephanie Tucker
- Club New Life Christian Ministry for Addiction and Recovery
- Lost & Found: Recovery in Christ by Bruce Stanley
- Overcoming Emotional Obstacles through Faith: Navigating the Mind Field by Anthony Acampora, Director of Banyan’s Faith in Recovery Program
- The Case for Christ by Lee Strobel
Mental Health Resources for Recovery
Lumina Recovery consist of both mental health and substance abuse treatment facilities, meaning we offer mental health resources as well as chemical dependency resources. What’s more, addiction often co-occurs with mental illness, making these resources ever more important.
Below are some resources for mental health recovery that can help you or your loved one:
- This Emotional Life video series
- No Kidding, Me 2!! with Joe Pantoliano
- Dare: The New Way to End Anxiety and Stop Panic Attacks by Barry McDonagh
- Pleasure Unwoven: An Explanation of the Brain Disease of Addiction by Kevin McCauley
- Declutter Your Mind: How to Stop Worrying, Relieve Anxiety, and Eliminate Negative Thinking by S.J. Scott and Barrie Davenport
Call Us Today – (877) 716-7515

